Quinn Raber arrived at a San Francisco bus station lugging a canvas bag containing all of his belongings: jeans, socks, underwear, pajamas. It was 1pm on a typically overcast day in August.
An unassuming 27-year-old, Raber seemed worn down: his skin was sun-reddened, he was unshaven, and a hat was pulled over his ruffled blond hair. After showing the driver a one-way ticket purchased for him by the city of San Francisco, he climbed the steps of the Greyhound bus.
He traveled 2,275 miles over three days to reach his destination: Indianapolis.
 Cities have been offering homeless people free bus tickets to relocate elsewhere for at least three decades. In recent years, homeless relocation programs have become more common, sprouting up in new cities across the country and costing the public millions of dollars.
Cities have been offering homeless people free bus tickets to relocate elsewhere for at least three decades. In recent years, homeless relocation programs have become more common, sprouting up in new cities across the country and costing the public millions of dollars.
But until now there has never been a systematic, nationwide assessment of the consequences. Where are these people being moved to? What impact are these programs having on the cities that send and the cities that receive them? And what happens to these homeless people after they reach their destination?
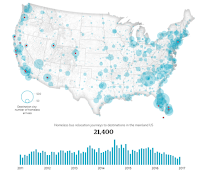
In an 18-month investigation, the Guardian has conducted the first detailed analysis of America’s homeless relocation programs, compiling a database of around 34,240 journeys and analyzing their effect on cities and people.
A count earlier this year found half a million homeless people on one night in America. The problem is most severe in the west, where rates of homelessness are skyrocketing in a number of major cities, and where states like California, Nevada, Oregon and Washington have some of the highest rates of per capita homelessness.
These are also the states where homeless relocation programs are concentrated. Using public record laws, the Guardian obtained data from 16 cities and counties that give homeless people free bus tickets to live elsewhere.
The data from these cities has been compiled to build the first comprehensive picture of America’s homeless relocation programs. Over the past six years, the period for which our data is most complete, we are able to track where more than 20,000 homeless people have been sent to and from within the mainland US. (...)
Some of these journeys provide a route out of homelessness, and many recipients of free tickets said they are grateful for the opportunity for a fresh start. Returning to places they previously lived, many rediscover old support networks, finding a safe place to sleep, caring friends or family, and the stepping stones that lead, eventually, to their own home.
Nan Roman, head of the National Alliance to End Homelessness, said bus programs can be a “positive”, although not a panacea, in part because most people are homeless in places they are from.
That is far from the whole story, however.
While the stated goal of San Francisco’s Homeward Bound and similar programs is helping people, the schemes also serve the interests of cities, which view free bus tickets as a cheap and effective way of cutting their homeless populations.
People are routinely sent thousands of miles away after only a cursory check by authorities to establish they have a suitable place to stay once they get there. Some said they feel pressured into taking tickets, and others described ending up on the streets within weeks of their arrival.
Jeff Weinberger, co-founder of the Florida Homelessness Action Coalition, a not-for-profit that operates in a state with four bus programs, said the schemes are a “smoke-and-mirrors ruse tantamount to shifting around the deck chairs on the Titanic rather than reducing homelessness”.
“Once they get you out of their city, they really don’t care what happens to you.”
by Outside in America Team, The Guardian | Read more:
Image: The Guardian
An unassuming 27-year-old, Raber seemed worn down: his skin was sun-reddened, he was unshaven, and a hat was pulled over his ruffled blond hair. After showing the driver a one-way ticket purchased for him by the city of San Francisco, he climbed the steps of the Greyhound bus.
He traveled 2,275 miles over three days to reach his destination: Indianapolis.
 Cities have been offering homeless people free bus tickets to relocate elsewhere for at least three decades. In recent years, homeless relocation programs have become more common, sprouting up in new cities across the country and costing the public millions of dollars.
Cities have been offering homeless people free bus tickets to relocate elsewhere for at least three decades. In recent years, homeless relocation programs have become more common, sprouting up in new cities across the country and costing the public millions of dollars.But until now there has never been a systematic, nationwide assessment of the consequences. Where are these people being moved to? What impact are these programs having on the cities that send and the cities that receive them? And what happens to these homeless people after they reach their destination?
In an 18-month investigation, the Guardian has conducted the first detailed analysis of America’s homeless relocation programs, compiling a database of around 34,240 journeys and analyzing their effect on cities and people.
A count earlier this year found half a million homeless people on one night in America. The problem is most severe in the west, where rates of homelessness are skyrocketing in a number of major cities, and where states like California, Nevada, Oregon and Washington have some of the highest rates of per capita homelessness.
These are also the states where homeless relocation programs are concentrated. Using public record laws, the Guardian obtained data from 16 cities and counties that give homeless people free bus tickets to live elsewhere.
The data from these cities has been compiled to build the first comprehensive picture of America’s homeless relocation programs. Over the past six years, the period for which our data is most complete, we are able to track where more than 20,000 homeless people have been sent to and from within the mainland US. (...)
Some of these journeys provide a route out of homelessness, and many recipients of free tickets said they are grateful for the opportunity for a fresh start. Returning to places they previously lived, many rediscover old support networks, finding a safe place to sleep, caring friends or family, and the stepping stones that lead, eventually, to their own home.
Nan Roman, head of the National Alliance to End Homelessness, said bus programs can be a “positive”, although not a panacea, in part because most people are homeless in places they are from.
That is far from the whole story, however.
While the stated goal of San Francisco’s Homeward Bound and similar programs is helping people, the schemes also serve the interests of cities, which view free bus tickets as a cheap and effective way of cutting their homeless populations.
People are routinely sent thousands of miles away after only a cursory check by authorities to establish they have a suitable place to stay once they get there. Some said they feel pressured into taking tickets, and others described ending up on the streets within weeks of their arrival.
Jeff Weinberger, co-founder of the Florida Homelessness Action Coalition, a not-for-profit that operates in a state with four bus programs, said the schemes are a “smoke-and-mirrors ruse tantamount to shifting around the deck chairs on the Titanic rather than reducing homelessness”.
“Once they get you out of their city, they really don’t care what happens to you.”
by Outside in America Team, The Guardian | Read more:
Image: The Guardian