Claude Lalanne,‘Ginkgo’ Chairs, 1999
via:
Showing posts with label Design. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Design. Show all posts
Tuesday, February 24, 2026
Friday, February 20, 2026
Kung Fu Robots Steal the Show
Dozens of G1 robots from Unitree Robotics delivered the world's first fully autonomous humanoid robot kung fu performance, featuring rapid position changes. The show pushed the limits of robotic movement and set multiple global records.
[ed. Not your mom's old roomba anymore. Robotics + AI the next frontier.]
Tuesday, February 10, 2026
Claude's New Constitution
We’re publishing a new constitution for our AI model, Claude. It’s a detailed description of Anthropic’s vision for Claude’s values and behavior; a holistic document that explains the context in which Claude operates and the kind of entity we would like Claude to be.
The constitution is a crucial part of our model training process, and its content directly shapes Claude’s behavior. Training models is a difficult task, and Claude’s outputs might not always adhere to the constitution’s ideals. But we think that the way the new constitution is written—with a thorough explanation of our intentions and the reasons behind them—makes it more likely to cultivate good values during training.
In this post, we describe what we’ve included in the new constitution and some of the considerations that informed our approach...
What is Claude’s Constitution?
Claude’s constitution is the foundational document that both expresses and shapes who Claude is. It contains detailed explanations of the values we would like Claude to embody and the reasons why. In it, we explain what we think it means for Claude to be helpful while remaining broadly safe, ethical, and compliant with our guidelines. The constitution gives Claude information about its situation and offers advice for how to deal with difficult situations and tradeoffs, like balancing honesty with compassion and the protection of sensitive information. Although it might sound surprising, the constitution is written primarily for Claude. It is intended to give Claude the knowledge and understanding it needs to act well in the world.
We treat the constitution as the final authority on how we want Claude to be and to behave—that is, any other training or instruction given to Claude should be consistent with both its letter and its underlying spirit. This makes publishing the constitution particularly important from a transparency perspective: it lets people understand which of Claude’s behaviors are intended versus unintended, to make informed choices, and to provide useful feedback. We think transparency of this kind will become ever more important as AIs start to exert more influence in society1.
We use the constitution at various stages of the training process. This has grown out of training techniques we’ve been using since 2023, when we first began training Claude models using Constitutional AI. Our approach has evolved significantly since then, and the new constitution plays an even more central role in training.
Claude itself also uses the constitution to construct many kinds of synthetic training data, including data that helps it learn and understand the constitution, conversations where the constitution might be relevant, responses that are in line with its values, and rankings of possible responses. All of these can be used to train future versions of Claude to become the kind of entity the constitution describes. This practical function has shaped how we’ve written the constitution: it needs to work both as a statement of abstract ideals and a useful artifact for training.
Our new approach to Claude’s Constitution
Our previous Constitution was composed of a list of standalone principles. We’ve come to believe that a different approach is necessary. We think that in order to be good actors in the world, AI models like Claude need to understand why we want them to behave in certain ways, and we need to explain this to them rather than merely specify what we want them to do. If we want models to exercise good judgment across a wide range of novel situations, they need to be able to generalize—to apply broad principles rather than mechanically following specific rules.
Specific rules and bright lines sometimes have their advantages. They can make models’ actions more predictable, transparent, and testable, and we do use them for some especially high-stakes behaviors in which Claude should never engage (we call these “hard constraints”). But such rules can also be applied poorly in unanticipated situations or when followed too rigidly2. We don’t intend for the constitution to be a rigid legal document—and legal constitutions aren’t necessarily like this anyway.
The constitution reflects our current thinking about how to approach a dauntingly novel and high-stakes project: creating safe, beneficial non-human entities whose capabilities may come to rival or exceed our own. Although the document is no doubt flawed in many ways, we want it to be something future models can look back on and see as an honest and sincere attempt to help Claude understand its situation, our motives, and the reasons we shape Claude in the ways we do.
The constitution is a crucial part of our model training process, and its content directly shapes Claude’s behavior. Training models is a difficult task, and Claude’s outputs might not always adhere to the constitution’s ideals. But we think that the way the new constitution is written—with a thorough explanation of our intentions and the reasons behind them—makes it more likely to cultivate good values during training.
In this post, we describe what we’ve included in the new constitution and some of the considerations that informed our approach...
What is Claude’s Constitution?
Claude’s constitution is the foundational document that both expresses and shapes who Claude is. It contains detailed explanations of the values we would like Claude to embody and the reasons why. In it, we explain what we think it means for Claude to be helpful while remaining broadly safe, ethical, and compliant with our guidelines. The constitution gives Claude information about its situation and offers advice for how to deal with difficult situations and tradeoffs, like balancing honesty with compassion and the protection of sensitive information. Although it might sound surprising, the constitution is written primarily for Claude. It is intended to give Claude the knowledge and understanding it needs to act well in the world.
We treat the constitution as the final authority on how we want Claude to be and to behave—that is, any other training or instruction given to Claude should be consistent with both its letter and its underlying spirit. This makes publishing the constitution particularly important from a transparency perspective: it lets people understand which of Claude’s behaviors are intended versus unintended, to make informed choices, and to provide useful feedback. We think transparency of this kind will become ever more important as AIs start to exert more influence in society1.
We use the constitution at various stages of the training process. This has grown out of training techniques we’ve been using since 2023, when we first began training Claude models using Constitutional AI. Our approach has evolved significantly since then, and the new constitution plays an even more central role in training.
Claude itself also uses the constitution to construct many kinds of synthetic training data, including data that helps it learn and understand the constitution, conversations where the constitution might be relevant, responses that are in line with its values, and rankings of possible responses. All of these can be used to train future versions of Claude to become the kind of entity the constitution describes. This practical function has shaped how we’ve written the constitution: it needs to work both as a statement of abstract ideals and a useful artifact for training.
Our new approach to Claude’s Constitution
Our previous Constitution was composed of a list of standalone principles. We’ve come to believe that a different approach is necessary. We think that in order to be good actors in the world, AI models like Claude need to understand why we want them to behave in certain ways, and we need to explain this to them rather than merely specify what we want them to do. If we want models to exercise good judgment across a wide range of novel situations, they need to be able to generalize—to apply broad principles rather than mechanically following specific rules.
Specific rules and bright lines sometimes have their advantages. They can make models’ actions more predictable, transparent, and testable, and we do use them for some especially high-stakes behaviors in which Claude should never engage (we call these “hard constraints”). But such rules can also be applied poorly in unanticipated situations or when followed too rigidly2. We don’t intend for the constitution to be a rigid legal document—and legal constitutions aren’t necessarily like this anyway.
The constitution reflects our current thinking about how to approach a dauntingly novel and high-stakes project: creating safe, beneficial non-human entities whose capabilities may come to rival or exceed our own. Although the document is no doubt flawed in many ways, we want it to be something future models can look back on and see as an honest and sincere attempt to help Claude understand its situation, our motives, and the reasons we shape Claude in the ways we do.
by Anthropic | Read more:
Image: Anthropic
[ed. I have an inclination to distrust AI companies, mostly because their goals (other than advancing technology) appear strongly directed at achieving market dominance and winning some (undefined) race to AGI. Anthropic is different. They actually seem legitimately concerned with the ethical implications of building another bomb that could potentially destroy humanity, or at minimum a large degree of human agency, and are aware of the responsibilities that go along with that. This is a well thought out and necessary document that hopefully other companies will follow and improve on, and that governments can use to develop more well-informed regulatory oversight in the future. See also: The New Politics of the AI Apocalypse; and, The Anthropic Hive Mind (Medim).
Labels:
Business,
Critical Thought,
Design,
Education,
Philosophy,
Psychology,
Relationships,
Technology
Thursday, February 5, 2026
The Questionable Science Behind the Odd-Looking Football Helmets
The N.F.L. claims Guardian Caps reduce the risk of concussions. The company that makes them says, “It has nothing to do with concussions.”
The first time Jared Wilson, a New England Patriots offensive lineman, is seen on the Super Bowl broadcast on Sunday, some viewers may wonder why he has such a big helmet.
It’s called a Guardian Cap, and Mr. Wilson is among about two dozen National Football League players who have worn the helmet covering in games this season. Not for comfort or style. Even the company that makes the cap acknowledges that it’s bulky and ugly. Rather, Wilson and others have worn it for its purported safety benefits.
The N.F.L. claims the cartoonish caps reduce the risk of getting a concussion, convincing some players that they are worth wearing. The company that designed and manufactures Guardian Caps, though, makes no such claim.
“No helmet, headgear or chin strap can prevent or eliminate the risk of concussions or other serious head injuries while playing sports or otherwise,” the product’s disclaimer warns. Instead, the company says its caps blunt the impact of smaller hits to the head that are linked to long-term brain damage.
“It has nothing to do with concussions,” said Erin Hanson, a co-founder of Guardian Sports, the Atlanta-area company that makes the cap. “We call concussions ‘the C word.’ This is about reducing the impact of all those hits every time. That’s all that was.”
The disconnect between the N.F.L.’s claims about the Guardian Caps and what the company promises is emblematic of the messy line between promotion and protection, and the power of the N.F.L. to sway football coaches and players trying to insulate themselves from the dangers of the sport.
An endorsement by the N.F.L., the country’s most visible and powerful sports league, can generate millions of dollars in sales for equipment makers, including Guardian Sports. The N.F.L.’s embrace of the caps, beginning in 2022, has led to a surge in orders from youth leagues to pro teams. About half a million players at all levels now wear them, Guardian Sports said.
“Anything I can do to save my brain, save my head,” said Kevin Dotson, an offensive lineman on the Los Angeles Rams who has worn the cap in games since last season.
Ms. Hanson said the company had struggled with whether to promote the N.F.L.’s claims about concussions. It decided to do so because the N.F.L.’s boasts might persuade young players to use the product, even if the benefits are not comparable. (...)
Guardian Caps are the latest in a wave of products that have emerged since researchers linked the sport to the progressive brain disease known as chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or C.T.E. Scores of companies have introduced equipment that purports to prevent head injuries, from a silicone collar worn around a player’s neck, known as the Q-Collar, which is promoted as a way to give the brain an extra layer of cushioning, to G8RSkin Shiesty, a head covering that is worn under helmets and promises to significantly reduce concussion risk.
Independent neurologists are generally skeptical, if not outright dismissive, of the benefits of any product claiming to reduce concussions because few rigorous studies have been done to demonstrate their effectiveness.
Few products have received as much publicity as the Guardian Cap, though. Sales of the caps, which were introduced in 2012, took off after the company won the N.F.L.’s HeadHealthTECH Challenge in 2017 — two years after the league settled a lawsuit brought by more than 5,000 former players who accused the N.F.L. of hiding from them the dangers of concussions.
Guardian Sports received $20,000 from the league for additional testing, but the N.F.L.’s endorsement was priceless.
Orders for the caps from colleges, high schools and youth teams poured in. Nearly every college team in the top ranks practices with the caps. In 2021, researchers, including some affiliated with the N.F.L. and its players’ union, published a paper that said Guardian Caps reduced “head impact severity” by 9 percent.
That year, Guardian Sports introduced its NXT model, with an extra layer of padding for bigger, stronger players. The N.F.L. required linemen, tight ends and linebackers to wear them in training camp. In 2023, the mandate expanded to all contact practices, and running backs and fullbacks were added. Starting in 2024, wide receivers and defensive backs had to wear them in practices, and players could wear them in games. (...)
Researchers at Virginia Tech, which runs a well-regarded helmet-testing laboratory, found that players who wore the NXT version of the Guardian Cap experienced a 14 percent decline in rotational accelerations — basically, the turning of the head — and that their concussion risk was 34 percent lower than for players who wore only helmets.
The benefits were significantly lower for players who wore the XT, the model worn in youth leagues and high schools. Rotational acceleration was only 5 percent lower, and the concussion risk was reduced by 15 percent.
Stefan Duma, who leads the lab, said the smaller reductions, combined with better helmets and fewer full contact practices, suggested that the benefits of wearing the XT were negligible.
“We tested it thoroughly, and the benefits are just not there,” Dr. Duma said. “It’s all noise, no statistical difference in youth.”
Most parents and coaches, though, do not read research reports from testing labs, and there is little information on the Guardian Sports website that explains the difference in performance between the XT and NXT models. But looking at the testimonials on the website from Mr. Goodell and other N.F.L. luminaries, parents and coaches might believe they were buying the cap worn by the pros.
It’s called a Guardian Cap, and Mr. Wilson is among about two dozen National Football League players who have worn the helmet covering in games this season. Not for comfort or style. Even the company that makes the cap acknowledges that it’s bulky and ugly. Rather, Wilson and others have worn it for its purported safety benefits.
The N.F.L. claims the cartoonish caps reduce the risk of getting a concussion, convincing some players that they are worth wearing. The company that designed and manufactures Guardian Caps, though, makes no such claim.
“No helmet, headgear or chin strap can prevent or eliminate the risk of concussions or other serious head injuries while playing sports or otherwise,” the product’s disclaimer warns. Instead, the company says its caps blunt the impact of smaller hits to the head that are linked to long-term brain damage.
“It has nothing to do with concussions,” said Erin Hanson, a co-founder of Guardian Sports, the Atlanta-area company that makes the cap. “We call concussions ‘the C word.’ This is about reducing the impact of all those hits every time. That’s all that was.”
The disconnect between the N.F.L.’s claims about the Guardian Caps and what the company promises is emblematic of the messy line between promotion and protection, and the power of the N.F.L. to sway football coaches and players trying to insulate themselves from the dangers of the sport.
An endorsement by the N.F.L., the country’s most visible and powerful sports league, can generate millions of dollars in sales for equipment makers, including Guardian Sports. The N.F.L.’s embrace of the caps, beginning in 2022, has led to a surge in orders from youth leagues to pro teams. About half a million players at all levels now wear them, Guardian Sports said.
“Anything I can do to save my brain, save my head,” said Kevin Dotson, an offensive lineman on the Los Angeles Rams who has worn the cap in games since last season.
The league claimed that the Guardian Cap had helped reduce concussions by more than 50 percent, which has put the company in the awkward position of embracing the spirit of the endorsement while distancing itself from the facts of it. Further complicating the situation: The model worn by pro and college players, the NXT, is not the same as the company’s mass-market product, the XT, which retails for $75. That model has less padding than the NXT, and may be less effective at limiting the impact of hits to the head, studies have shown.
Ms. Hanson said the company had struggled with whether to promote the N.F.L.’s claims about concussions. It decided to do so because the N.F.L.’s boasts might persuade young players to use the product, even if the benefits are not comparable. (...)
Guardian Caps are the latest in a wave of products that have emerged since researchers linked the sport to the progressive brain disease known as chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or C.T.E. Scores of companies have introduced equipment that purports to prevent head injuries, from a silicone collar worn around a player’s neck, known as the Q-Collar, which is promoted as a way to give the brain an extra layer of cushioning, to G8RSkin Shiesty, a head covering that is worn under helmets and promises to significantly reduce concussion risk.
Independent neurologists are generally skeptical, if not outright dismissive, of the benefits of any product claiming to reduce concussions because few rigorous studies have been done to demonstrate their effectiveness.
Few products have received as much publicity as the Guardian Cap, though. Sales of the caps, which were introduced in 2012, took off after the company won the N.F.L.’s HeadHealthTECH Challenge in 2017 — two years after the league settled a lawsuit brought by more than 5,000 former players who accused the N.F.L. of hiding from them the dangers of concussions.
Guardian Sports received $20,000 from the league for additional testing, but the N.F.L.’s endorsement was priceless.
Orders for the caps from colleges, high schools and youth teams poured in. Nearly every college team in the top ranks practices with the caps. In 2021, researchers, including some affiliated with the N.F.L. and its players’ union, published a paper that said Guardian Caps reduced “head impact severity” by 9 percent.
That year, Guardian Sports introduced its NXT model, with an extra layer of padding for bigger, stronger players. The N.F.L. required linemen, tight ends and linebackers to wear them in training camp. In 2023, the mandate expanded to all contact practices, and running backs and fullbacks were added. Starting in 2024, wide receivers and defensive backs had to wear them in practices, and players could wear them in games. (...)
Researchers at Virginia Tech, which runs a well-regarded helmet-testing laboratory, found that players who wore the NXT version of the Guardian Cap experienced a 14 percent decline in rotational accelerations — basically, the turning of the head — and that their concussion risk was 34 percent lower than for players who wore only helmets.
The benefits were significantly lower for players who wore the XT, the model worn in youth leagues and high schools. Rotational acceleration was only 5 percent lower, and the concussion risk was reduced by 15 percent.
Stefan Duma, who leads the lab, said the smaller reductions, combined with better helmets and fewer full contact practices, suggested that the benefits of wearing the XT were negligible.
“We tested it thoroughly, and the benefits are just not there,” Dr. Duma said. “It’s all noise, no statistical difference in youth.”
Most parents and coaches, though, do not read research reports from testing labs, and there is little information on the Guardian Sports website that explains the difference in performance between the XT and NXT models. But looking at the testimonials on the website from Mr. Goodell and other N.F.L. luminaries, parents and coaches might believe they were buying the cap worn by the pros.
by Ken Belson, NY Times | Read more:
Images: Audra Melton, NYT; Cooper Neill/Getty
Images: Audra Melton, NYT; Cooper Neill/Getty
Wednesday, February 4, 2026
In Praise of Urban Disorder
In his essay “Planning for an Unplanned City,” Jason Thorne, Toronto’s chief planner, poses a pair of provocative questions to his colleagues. “Have our rules and regulations squeezed too much of the life out of our cities?” he asks. “But also how do you plan and design a city that is safe and functional while also leaving room for spontaneity and serendipity?”
This premise — that urban planning’s efforts to impose order risk editing out the culture, character, complexity and creative friction that makes cities cities — is a guiding theme in Messy Cities: Why We Can’t Plan Everything, a collection of essays, including Thorne’s, gathered by Toronto-based editors Zahra Ebrahim, Leslie Woo, Dylan Reid and John Lorinc. In it, they argue that “messiness is an essential element of the city.” Case studies from around the world show how imperfection can be embraced, created and preserved, from the informal street eateries of East Los Angeles to the sports facilities carved out of derelict spaces in Mumbai.
Embracing urban disorder might seem like an unlikely cause. But Woo, an urban planner and chief executive officer of the Toronto-based nonprofit CivicAction, and Reid, executive editor of Spacing magazine, offer up a series of questions that get at the heart of debates surrounding messy urbanism. In an essay about street art, they ask, “Is it ugly or creative? Does it bring disruption or diversity? Should it be left to emerge from below or be managed from above? Is it permanent or ephemeral? Does it benefit communities or just individuals? Does it create opportunity or discomfort? Are there limits around it and if so can they be effective?”
Bloomberg CityLab caught up with Woo and Ebrahim, cofounder of the public interest design studio Monumental, about why messiness in cities can be worth advocating for, and how to let the healthy kind flourish. The conversation has been edited and condensed for clarity.
You intentionally don’t give a specific definition for messy urbanism in the book, making the case that to do so would be antithetical to the idea itself. But if you were to give a general overview of the qualities and attributes you’d ascribe to messy cities, what would they be?
Leslie Woo: All of the authors included in the book brought to it some form of two things — wanting to have a sense of belonging in the places they live and trying to understand how they can have agency in their community. And what comes out of that are acts of defiance that manifest both as tiny and intimate experiences and as big gestures in cities.
Zahra Ebrahim: I think of it as where institutions end and people begin. It’s about agency. So much of the “messy” defiance is people trying to live within their cultures and identities in ways that cities don’t always create space for. We’re not trying to fetishize messiness, but we do want to acknowledge that when people feel that agency, cities become more vibrant, spontaneous and delightful.
LW: I think of the story urban planning professor Nina-Marie Lister, director of Toronto’s Ecological Design Lab, tells about fighting to keep her wild front yard habitat garden after being ordered to cut it down by the city. There was a bylaw in place intended by the municipality to control what it deemed “noxious vegetation” on private property. Lister ended up doing a public advocacy campaign to get the bylaw updated.
The phrase “messy cities” could be construed negatively but it seems like a real term of affection for the editors and authors of this book. What does it represent to you?
ZE: You can see it represented in the Bloordale neighborhood of Toronto. During lockdown in 2020, a group of local residents came together and turned a large, gravel-filled site of a demolished school into an unexpected shared space for social distancing. With handmade signage, they cheekily named the site “Bloordale Beach.” Over weeks, they and others in the community organically and spontaneously brought this imagined, landlocked beach to life, adding beach chairs, “swimming guidelines” around the puddle that had formed after a storm, even a “barkour” area for local dogs. It was both a “messy” community art project and third space, but also a place for residents to demonstrate their agency and find joy in an uncertain and difficult time.
LW: The thing that is delightful about this topic is many of these efforts are exercises in reimagining cities. Individuals and groups see a space and approach it in a different way with a spirit and ingenuity that we don’t see enough of. It’s an exercise in thinking about how we want to live. I also want to make the point that we aren’t advocating for more chaos and confusion but rather showing how these groups are attempting to make sense of where they live.
ZE: Messiness has become a wedge issue — a way to pronounce and lean into existing political cleavages. Across the world we see politicians pointing to the challenges cities face — housing affordability, transit accessibility, access to employment — and wrongfully blame or attribute these urban “messes” to specific populations and groups. We see this in the rising anti-immigrant rhetoric we hear all over the world. As an editing team, I think there was a shared understanding that multicultural and diverse societies are more successful and that when we have to navigate shared social and cultural space, it’s better for society.
This is also not all about the failure of institutions to serve the needs of the public. Some of this is about groups responding to failures of the present and shaping a better future. And some of what we’re talking about is people seeing opportunities to make the type of “mess” that would support their community to thrive, like putting a pop-up market and third space in a strip mall parking lot, and creating a space for people to come together.
You and the rest of the editors are based in Toronto and the city comes up recurrently in the book. What makes the city such an interesting case study in messy urbanism?
ZE: Toronto is what a local journalist, Doug Saunders, calls an “arrival city” — one in three newcomers in Canada land in Toronto. These waves of migration are encoded in our city’s DNA. I think of a place like Kensington Market, where there have been successive arrivals of immigrants each decade, from Jewish and Eastern European and Italian immigrants in the early 1900s to Caribbean and Chinese immigrants in the 1960s and ’70s.
Kensington continues to be one of the most vibrant urban spaces in the city. You’ve got the market, food vendors, shops and semi-informal commercial activity, cultural venues and jazz bars. In so many parts of Toronto you can’t see the history on the street but in Kensington you can see the palimpsest and layers of change it’s lived through. There is development pressure in every direction and major retailers opening nearby but it remains this vibrant representation of different eras of newcomers in Toronto and what they needed — socially, culturally and commercially. It’s a great example of where the formal and informal, the planned and unplanned meet. Every nook and cranny is filled with a story, with locals making a “mess,” but really just expressing their agency.
LW: This messy urbanism can also be seen in Toronto’s apartment tower communities that were built in the 1960s. These buildings have experienced periods of neglect and changes in ownership. But today when moving from floor to floor, it feels like traveling around the entire world; you can move from the Caribbean to continental Africa to the Middle East. These are aerial cities in and of themselves. They’re a great example of people taking a place where the conditions aren’t ideal and telling their own different story — it’s everything from the music to the food to the languages.
You didn’t include any case studies or essays from Europe in the book. Why did you make that choice, and what does an overreliance on looking to cities like Copenhagen do to the way we think of and plan for cities?
LW: When I trained as an urban planner and architect, all the pedagogy was very Eurocentric — it was Spain, France and Greece. But if we want to reframe how we think about cities, we need to reframe our points of reference.
ZE: During our editorial meetings we talked about how the commonly accepted ideas about urban order that we know are Eurocentric by design, and don’t represent the multitude of people that live in cities and what “order” may mean to them. Again, it’s not to celebrate chaos but rather to say there are different mental models of what orderliness and messiness can look like.
Go to a place like Delhi and look at the way traffic roundabouts function. There are pedestrians and cars and everybody is moving in the direction they need to move in, it’s like a river of mobility. If you’re sitting in the back of a taxi coming from North America, it looks like chaos, but to the people that live there it’s just how the city moves.
In a chapter about Mexico City’s apartment architecture, Daniel Gordon talks about what it can teach us about how to create interesting streets and neighborhoods by becoming less attached to overly prescriptive planning and instead embracing a mix of ground-floor uses and buildings with varying materials and color palettes, setbacks and heights. He argues that design guidelines can negate creativity and expression in the built environment.
In another chapter, urban geography professor Andre Sorensen talks about Tokyo, which despite being perceived as a spontaneously messy city actually operates under one of the strictest zoning systems in the world. Built forms are highly regulated, but land use mix and subdivision controls aren’t. It’s yet another example of how different urban cultures and regulatory systems work to different sets of values and conceptions of order and disorder. We tried to pay closer attention to case studies that expanded the aperture of what North American urbanism typically covers.
by Rebecca Greenwald, Bloomberg | Read more:
Image:Alfredo Martinez/Getty Images
This premise — that urban planning’s efforts to impose order risk editing out the culture, character, complexity and creative friction that makes cities cities — is a guiding theme in Messy Cities: Why We Can’t Plan Everything, a collection of essays, including Thorne’s, gathered by Toronto-based editors Zahra Ebrahim, Leslie Woo, Dylan Reid and John Lorinc. In it, they argue that “messiness is an essential element of the city.” Case studies from around the world show how imperfection can be embraced, created and preserved, from the informal street eateries of East Los Angeles to the sports facilities carved out of derelict spaces in Mumbai.
Embracing urban disorder might seem like an unlikely cause. But Woo, an urban planner and chief executive officer of the Toronto-based nonprofit CivicAction, and Reid, executive editor of Spacing magazine, offer up a series of questions that get at the heart of debates surrounding messy urbanism. In an essay about street art, they ask, “Is it ugly or creative? Does it bring disruption or diversity? Should it be left to emerge from below or be managed from above? Is it permanent or ephemeral? Does it benefit communities or just individuals? Does it create opportunity or discomfort? Are there limits around it and if so can they be effective?”
Bloomberg CityLab caught up with Woo and Ebrahim, cofounder of the public interest design studio Monumental, about why messiness in cities can be worth advocating for, and how to let the healthy kind flourish. The conversation has been edited and condensed for clarity.
You intentionally don’t give a specific definition for messy urbanism in the book, making the case that to do so would be antithetical to the idea itself. But if you were to give a general overview of the qualities and attributes you’d ascribe to messy cities, what would they be?
Leslie Woo: All of the authors included in the book brought to it some form of two things — wanting to have a sense of belonging in the places they live and trying to understand how they can have agency in their community. And what comes out of that are acts of defiance that manifest both as tiny and intimate experiences and as big gestures in cities.
Zahra Ebrahim: I think of it as where institutions end and people begin. It’s about agency. So much of the “messy” defiance is people trying to live within their cultures and identities in ways that cities don’t always create space for. We’re not trying to fetishize messiness, but we do want to acknowledge that when people feel that agency, cities become more vibrant, spontaneous and delightful.
LW: I think of the story urban planning professor Nina-Marie Lister, director of Toronto’s Ecological Design Lab, tells about fighting to keep her wild front yard habitat garden after being ordered to cut it down by the city. There was a bylaw in place intended by the municipality to control what it deemed “noxious vegetation” on private property. Lister ended up doing a public advocacy campaign to get the bylaw updated.
The phrase “messy cities” could be construed negatively but it seems like a real term of affection for the editors and authors of this book. What does it represent to you?
ZE: You can see it represented in the Bloordale neighborhood of Toronto. During lockdown in 2020, a group of local residents came together and turned a large, gravel-filled site of a demolished school into an unexpected shared space for social distancing. With handmade signage, they cheekily named the site “Bloordale Beach.” Over weeks, they and others in the community organically and spontaneously brought this imagined, landlocked beach to life, adding beach chairs, “swimming guidelines” around the puddle that had formed after a storm, even a “barkour” area for local dogs. It was both a “messy” community art project and third space, but also a place for residents to demonstrate their agency and find joy in an uncertain and difficult time.
LW: The thing that is delightful about this topic is many of these efforts are exercises in reimagining cities. Individuals and groups see a space and approach it in a different way with a spirit and ingenuity that we don’t see enough of. It’s an exercise in thinking about how we want to live. I also want to make the point that we aren’t advocating for more chaos and confusion but rather showing how these groups are attempting to make sense of where they live.
ZE: Messiness has become a wedge issue — a way to pronounce and lean into existing political cleavages. Across the world we see politicians pointing to the challenges cities face — housing affordability, transit accessibility, access to employment — and wrongfully blame or attribute these urban “messes” to specific populations and groups. We see this in the rising anti-immigrant rhetoric we hear all over the world. As an editing team, I think there was a shared understanding that multicultural and diverse societies are more successful and that when we have to navigate shared social and cultural space, it’s better for society.
This is also not all about the failure of institutions to serve the needs of the public. Some of this is about groups responding to failures of the present and shaping a better future. And some of what we’re talking about is people seeing opportunities to make the type of “mess” that would support their community to thrive, like putting a pop-up market and third space in a strip mall parking lot, and creating a space for people to come together.
You and the rest of the editors are based in Toronto and the city comes up recurrently in the book. What makes the city such an interesting case study in messy urbanism?
ZE: Toronto is what a local journalist, Doug Saunders, calls an “arrival city” — one in three newcomers in Canada land in Toronto. These waves of migration are encoded in our city’s DNA. I think of a place like Kensington Market, where there have been successive arrivals of immigrants each decade, from Jewish and Eastern European and Italian immigrants in the early 1900s to Caribbean and Chinese immigrants in the 1960s and ’70s.
Kensington continues to be one of the most vibrant urban spaces in the city. You’ve got the market, food vendors, shops and semi-informal commercial activity, cultural venues and jazz bars. In so many parts of Toronto you can’t see the history on the street but in Kensington you can see the palimpsest and layers of change it’s lived through. There is development pressure in every direction and major retailers opening nearby but it remains this vibrant representation of different eras of newcomers in Toronto and what they needed — socially, culturally and commercially. It’s a great example of where the formal and informal, the planned and unplanned meet. Every nook and cranny is filled with a story, with locals making a “mess,” but really just expressing their agency.
LW: This messy urbanism can also be seen in Toronto’s apartment tower communities that were built in the 1960s. These buildings have experienced periods of neglect and changes in ownership. But today when moving from floor to floor, it feels like traveling around the entire world; you can move from the Caribbean to continental Africa to the Middle East. These are aerial cities in and of themselves. They’re a great example of people taking a place where the conditions aren’t ideal and telling their own different story — it’s everything from the music to the food to the languages.
You didn’t include any case studies or essays from Europe in the book. Why did you make that choice, and what does an overreliance on looking to cities like Copenhagen do to the way we think of and plan for cities?
LW: When I trained as an urban planner and architect, all the pedagogy was very Eurocentric — it was Spain, France and Greece. But if we want to reframe how we think about cities, we need to reframe our points of reference.
ZE: During our editorial meetings we talked about how the commonly accepted ideas about urban order that we know are Eurocentric by design, and don’t represent the multitude of people that live in cities and what “order” may mean to them. Again, it’s not to celebrate chaos but rather to say there are different mental models of what orderliness and messiness can look like.
Go to a place like Delhi and look at the way traffic roundabouts function. There are pedestrians and cars and everybody is moving in the direction they need to move in, it’s like a river of mobility. If you’re sitting in the back of a taxi coming from North America, it looks like chaos, but to the people that live there it’s just how the city moves.
In a chapter about Mexico City’s apartment architecture, Daniel Gordon talks about what it can teach us about how to create interesting streets and neighborhoods by becoming less attached to overly prescriptive planning and instead embracing a mix of ground-floor uses and buildings with varying materials and color palettes, setbacks and heights. He argues that design guidelines can negate creativity and expression in the built environment.
In another chapter, urban geography professor Andre Sorensen talks about Tokyo, which despite being perceived as a spontaneously messy city actually operates under one of the strictest zoning systems in the world. Built forms are highly regulated, but land use mix and subdivision controls aren’t. It’s yet another example of how different urban cultures and regulatory systems work to different sets of values and conceptions of order and disorder. We tried to pay closer attention to case studies that expanded the aperture of what North American urbanism typically covers.
by Rebecca Greenwald, Bloomberg | Read more:
Image:Alfredo Martinez/Getty Images
[ed. Give me a messy city any day, or at least one with a few messy parts.]
Claude's New Constitution
We're publishing a new constitution for our AI model, Claude. It's a detailed description of Anthropic's vision for Claude's values and behavior; a holistic document that explains the context in which Claude operates and the kind of entity we would like Claude to be.
The constitution is a crucial part of our model training process, and its content directly shapes Claude's behavior. Training models is a difficult task, and Claude's outputs might not always adhere to the constitution's ideals. But we think that the way the new constitution is written—with a thorough explanation of our intentions and the reasons behind them—makes it more likely to cultivate good values during training.
In this post, we describe what we've included in the new constitution and some of the considerations that informed our approach.
We're releasing Claude's constitution in full under a Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Deed, meaning it can be freely used by anyone for any purpose without asking for permission.
What is Claude's Constitution?
Claude's constitution is the foundational document that both expresses and shapes who Claude is. It contains detailed explanations of the values we would like Claude to embody and the reasons why. In it, we explain what we think it means for Claude to be helpful while remaining broadly safe, ethical, and compliant with our guidelines. The constitution gives Claude information about its situation and offers advice for how to deal with difficult situations and tradeoffs, like balancing honesty with compassion and the protection of sensitive information. Although it might sound surprising, the constitution is written primarily for Claude. It is intended to give Claude the knowledge and understanding it needs to act well in the world.
We treat the constitution as the final authority on how we want Claude to be and to behave—that is, any other training or instruction given to Claude should be consistent with both its letter and its underlying spirit. This makes publishing the constitution particularly important from a transparency perspective: it lets people understand which of Claude's behaviors are intended versus unintended, to make informed choices, and to provide useful feedback. We think transparency of this kind will become ever more important as AIs start to exert more influence in society.
We use the constitution at various stages of the training process. This has grown out of training techniques we've been using since 2023, when we first began training Claude models using Constitutional AI. Our approach has evolved significantly since then, and the new constitution plays an even more central role in training.
Claude itself also uses the constitution to construct many kinds of synthetic training data, including data that helps it learn and understand the constitution, conversations where the constitution might be relevant, responses that are in line with its values, and rankings of possible responses. All of these can be used to train future versions of Claude to become the kind of entity the constitution describes. This practical function has shaped how we've written the constitution: it needs to work both as a statement of abstract ideals and a useful artifact for training.
Our new approach to Claude's Constitution
Our previous Constitution was composed of a list of standalone principles. We've come to believe that a different approach is necessary. We think that in order to be good actors in the world, AI models like Claude need to understand why we want them to behave in certain ways, and we need to explain this to them rather than merely specify what we want them to do. If we want models to exercise good judgment across a wide range of novel situations, they need to be able to generalize—to apply broad principles rather than mechanically following specific rules.
Specific rules and bright lines sometimes have their advantages. They can make models' actions more predictable, transparent, and testable, and we do use them for some especially high-stakes behaviors in which Claude should never engage (we call these "hard constraints"). But such rules can also be applied poorly in unanticipated situations or when followed too rigidly . We don't intend for the constitution to be a rigid legal document—and legal constitutions aren't necessarily like this anyway.
The constitution reflects our current thinking about how to approach a dauntingly novel and high-stakes project: creating safe, beneficial non-human entities whose capabilities may come to rival or exceed our own. Although the document is no doubt flawed in many ways, we want it to be something future models can look back on and see as an honest and sincere attempt to help Claude understand its situation, our motives, and the reasons we shape Claude in the ways we do.
A brief summary of the new constitution
In order to be both safe and beneficial, we want all current Claude models to be:
Most of the constitution is focused on giving more detailed explanations and guidance about these priorities. The main sections are as follows:
by Zac Hatfield-Dodds, Drake Thomas, Anthropic | Read more:
The constitution is a crucial part of our model training process, and its content directly shapes Claude's behavior. Training models is a difficult task, and Claude's outputs might not always adhere to the constitution's ideals. But we think that the way the new constitution is written—with a thorough explanation of our intentions and the reasons behind them—makes it more likely to cultivate good values during training.
In this post, we describe what we've included in the new constitution and some of the considerations that informed our approach.
We're releasing Claude's constitution in full under a Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Deed, meaning it can be freely used by anyone for any purpose without asking for permission.
What is Claude's Constitution?
Claude's constitution is the foundational document that both expresses and shapes who Claude is. It contains detailed explanations of the values we would like Claude to embody and the reasons why. In it, we explain what we think it means for Claude to be helpful while remaining broadly safe, ethical, and compliant with our guidelines. The constitution gives Claude information about its situation and offers advice for how to deal with difficult situations and tradeoffs, like balancing honesty with compassion and the protection of sensitive information. Although it might sound surprising, the constitution is written primarily for Claude. It is intended to give Claude the knowledge and understanding it needs to act well in the world.
We treat the constitution as the final authority on how we want Claude to be and to behave—that is, any other training or instruction given to Claude should be consistent with both its letter and its underlying spirit. This makes publishing the constitution particularly important from a transparency perspective: it lets people understand which of Claude's behaviors are intended versus unintended, to make informed choices, and to provide useful feedback. We think transparency of this kind will become ever more important as AIs start to exert more influence in society.
We use the constitution at various stages of the training process. This has grown out of training techniques we've been using since 2023, when we first began training Claude models using Constitutional AI. Our approach has evolved significantly since then, and the new constitution plays an even more central role in training.
Claude itself also uses the constitution to construct many kinds of synthetic training data, including data that helps it learn and understand the constitution, conversations where the constitution might be relevant, responses that are in line with its values, and rankings of possible responses. All of these can be used to train future versions of Claude to become the kind of entity the constitution describes. This practical function has shaped how we've written the constitution: it needs to work both as a statement of abstract ideals and a useful artifact for training.
Our new approach to Claude's Constitution
Our previous Constitution was composed of a list of standalone principles. We've come to believe that a different approach is necessary. We think that in order to be good actors in the world, AI models like Claude need to understand why we want them to behave in certain ways, and we need to explain this to them rather than merely specify what we want them to do. If we want models to exercise good judgment across a wide range of novel situations, they need to be able to generalize—to apply broad principles rather than mechanically following specific rules.
Specific rules and bright lines sometimes have their advantages. They can make models' actions more predictable, transparent, and testable, and we do use them for some especially high-stakes behaviors in which Claude should never engage (we call these "hard constraints"). But such rules can also be applied poorly in unanticipated situations or when followed too rigidly . We don't intend for the constitution to be a rigid legal document—and legal constitutions aren't necessarily like this anyway.
The constitution reflects our current thinking about how to approach a dauntingly novel and high-stakes project: creating safe, beneficial non-human entities whose capabilities may come to rival or exceed our own. Although the document is no doubt flawed in many ways, we want it to be something future models can look back on and see as an honest and sincere attempt to help Claude understand its situation, our motives, and the reasons we shape Claude in the ways we do.
A brief summary of the new constitution
In order to be both safe and beneficial, we want all current Claude models to be:
- Broadly safe: not undermining appropriate human mechanisms to oversee AI during the current phase of development;
- Broadly ethical: being honest, acting according to good values, and avoiding actions that are inappropriate, dangerous, or harmful;
- Compliant with Anthropic's guidelines: acting in accordance with more specific guidelines from Anthropic where relevant;
- Genuinely helpful: benefiting the operators and users they interact with.
Most of the constitution is focused on giving more detailed explanations and guidance about these priorities. The main sections are as follows:
by Zac Hatfield-Dodds, Drake Thomas, Anthropic | Read more:
[ed. Much respect for Anthropic who seem to be doing more for AI safety than anyone else in the industry. Hopefully, others will follow and refine this groundbreaking effort.
Labels:
Critical Thought,
Design,
Education,
Philosophy,
Psychology,
Relationships,
Technology
Tuesday, January 20, 2026
It's Not Normal
Samantha: This town has a weird smell that you're all probably used to…but I'm not.
Mrs Krabappel: It'll take you about six weeks, dear.-The Simpsons, "Bart's Friend Falls in Love," S3E23, May 7, 1992
We are living through weird times, and they've persisted for so long that you probably don't even notice it. But these times are not normal.
Now, I realize that this covers a lot of ground, and without detracting from all the other ways in which the world is weird and bad, I want to focus on one specific and pervasive and awful way in which this world is not normal, in part because this abnormality has a defined cause, a precise start date, and an obvious, actionable remedy.
6 years, 5 months and 22 days after Fox aired "Bart's Friend Falls in Love," Bill Clinton signed a new bill into law: the Digital Millennium Copyright Act of 1998 (DMCA).
Under Section 1201 of the DMCA, it's a felony to modify your own property in ways that the manufacturer disapproves of, even if your modifications accomplish some totally innocuous, legal, and socially beneficial goal. Not a little felony, either: DMCA 1201 provides for a five year sentence and a $500,000 fine for a first offense.
Back when the DMCA was being debated, its proponents insisted that their critics were overreacting. They pointed to the legal barriers to invoking DMCA 1201, and insisted that these new restrictions would only apply to a few marginal products in narrow ways that the average person would never even notice.
But that was obvious nonsense, obvious even in 1998, and far more obvious today, more than a quarter-century on. In order for a manufacturer to criminalize modifications to your own property, they have to satisfy two criteria: first, they must sell you a device with a computer in it; and second, they must design that computer with an "access control" that you have to work around in order to make a modification.
For example, say your toaster requires that you scan your bread before it will toast it, to make sure that you're only using a special, expensive kind of bread that kicks back a royalty to the manufacturer. If the embedded computer that does the scanning ships from the factory with a program that is supposed to prevent you from turning off the scanning step, then it is a felony to modify your toaster to work with "unauthorized bread":
If this sounds outlandish, then a) You definitely didn't walk the floor at CES last week, where there were a zillion "cooking robots" that required proprietary feedstock; and b) You haven't really thought hard about your iPhone (which will not allow you to install software of your choosing):
But back in 1998, computers – even the kind of low-powered computers that you'd embed in an appliance – were expensive and relatively rare. No longer! Today, manufacturers source powerful "System on a Chip" (SoC) processors at prices ranging from $0.25 to $8. These are full-fledged computers, easily capable of running an "access control" that satisfies DMCA 1201.
Likewise, in 1998, "access controls" (also called "DRM," "technical protection measures," etc) were a rarity in the field. That was because computer scientists broadly viewed these measures as useless. A determined adversary could always find a way around an access control, and they could package up that break as a software tool and costlessly, instantaneously distribute it over the internet to everyone in the world who wanted to do something that an access control impeded. Access controls were a stupid waste of engineering resources and a source of needless complexity and brittleness:
But – as critics pointed out in 1998 – chips were obviously going to get much cheaper, and if the US Congress made it a felony to bypass an access control, then every kind of manufacturer would be tempted to add some cheap SoCs to their products so they could add access controls and thereby felonize any uses of their products that cut into their profits. Basically, the DMCA offered manufacturers a bargain: add a dollar or two to the bill of materials for your product, and in return, the US government will imprison any competitors who offer your customers a "complementary good" that improves on it.
It's even worse than this: another thing that was obvious in 1998 was that once a manufacturer added a chip to a device, they would probably also figure out a way to connect it to the internet. Once that device is connected to the internet, the manufacturer can push software updates to it at will, which will be installed without user intervention. What's more, by using an access control in connection with that over-the-air update mechanism, the manufacturer can make it a felony to block its updates.
Which means that a manufacturer can sell you a device and then mandatorily update it at a later date to take away its functionality, and then sell that functionality back to you as a "subscription":
A thing that keeps happening:
And happening:
And happening:
In fact, it happens so often I've coined a term for it, "The Darth Vader MBA" (as in, "I'm altering the deal. Pray I don't alter it any further"):
Here's what this all means: any manufacturer who devotes a small amount of engineering work and incurs a small hardware expense can extinguish private property rights altogether.
What do I mean by private property? Well, we can look to Blackstone's 1753 treatise:
It's not just iPhones: versions of this play out in your medical implants (hearing aid, insulin pump, etc); appliances (stoves, fridges, washing machines); cars and ebikes; set-top boxes and game consoles; ebooks and streaming videos; small appliances (toothbrushes, TVs, speakers), and more.
Increasingly, things that you actually own are the exception, not the rule.
And this is not normal. The end of ownership represents an overturn of a foundation of modern civilization. The fact that the only "people" who can truly own something are the transhuman, immortal colony organisms we call "Limited Liability Corporations" is an absolutely surreal reversal of the normal order of things.
It's a reversal with deep implications: for one thing, it means that you can't protect yourself from raids on your private data or ready cash by adding privacy blockers to your device, which would make it impossible for airlines or ecommerce sites to guess about how rich/desperate you are before quoting you a "personalized price":
It also means you can't stop your device from leaking information about your movements, or even your conversations – Microsoft has announced that it will gather all of your private communications and ship them to its servers for use by "agentic AI": (...)
Microsoft has also confirmed that it provides US authorities with warrantless, secret access to your data:
This is deeply abnormal. Sure, greedy corporate control freaks weren't invented in the 21st century, but the laws that let those sociopaths put you in prison for failing to arrange your affairs to their benefit – and your own detriment – are.
But because computers got faster and cheaper over decades, the end of ownership has had an incremental rollout, and we've barely noticed that it's happened. Sure, we get irritated when our garage-door opener suddenly requires us to look at seven ads every time we use the app that makes it open or close:
But societally, we haven't connected that incident to this wider phenomenon. It stinks here, but we're all used to it.
It's not normal to buy a book and then not be able to lend it, sell it, or give it away. Lending, selling and giving away books is older than copyright. It's older than publishing. It's older than printing. It's older than paper. It is fucking weird (and also terrible) (obviously) that there's a new kind of very popular book that you can go to prison for lending, selling or giving away.
We're just a few cycles away from a pair of shoes that can figure out which shoelaces you're using, or a dishwasher that can block you from using third-party dishes:
It's not normal, and it has profound implications for our security, our privacy, and our society. It makes us easy pickings for corporate vampires who drain our wallets through the gadgets and tools we rely on. It makes us easy pickings for fascists and authoritarians who ally themselves with corporate vampires by promising them tax breaks in exchange for collusion in the destruction of a free society.
I know that these problems are more important than whether or not we think this is normal. But still. It. Is. Just. Not. Normal.
[ed. Anything labeled 'smart' is usually suspect. What's particularly dangerous is if successive generations fall prey to what conservation biology calls shifting baseline syndrome (forgetting or never really missing something that's been lost, so we don't grieve or fight to restore it). For a deep dive into why everything keeps getting worse see Mr. Doctorow's new book: Enshittification: Why Everything Suddenly Got Worse and What to Do About It," Farrar, Straus, Giroux, October 7 2025.]
Now, I realize that this covers a lot of ground, and without detracting from all the other ways in which the world is weird and bad, I want to focus on one specific and pervasive and awful way in which this world is not normal, in part because this abnormality has a defined cause, a precise start date, and an obvious, actionable remedy.
6 years, 5 months and 22 days after Fox aired "Bart's Friend Falls in Love," Bill Clinton signed a new bill into law: the Digital Millennium Copyright Act of 1998 (DMCA).
Under Section 1201 of the DMCA, it's a felony to modify your own property in ways that the manufacturer disapproves of, even if your modifications accomplish some totally innocuous, legal, and socially beneficial goal. Not a little felony, either: DMCA 1201 provides for a five year sentence and a $500,000 fine for a first offense.
Back when the DMCA was being debated, its proponents insisted that their critics were overreacting. They pointed to the legal barriers to invoking DMCA 1201, and insisted that these new restrictions would only apply to a few marginal products in narrow ways that the average person would never even notice.
But that was obvious nonsense, obvious even in 1998, and far more obvious today, more than a quarter-century on. In order for a manufacturer to criminalize modifications to your own property, they have to satisfy two criteria: first, they must sell you a device with a computer in it; and second, they must design that computer with an "access control" that you have to work around in order to make a modification.
For example, say your toaster requires that you scan your bread before it will toast it, to make sure that you're only using a special, expensive kind of bread that kicks back a royalty to the manufacturer. If the embedded computer that does the scanning ships from the factory with a program that is supposed to prevent you from turning off the scanning step, then it is a felony to modify your toaster to work with "unauthorized bread":
If this sounds outlandish, then a) You definitely didn't walk the floor at CES last week, where there were a zillion "cooking robots" that required proprietary feedstock; and b) You haven't really thought hard about your iPhone (which will not allow you to install software of your choosing):
But back in 1998, computers – even the kind of low-powered computers that you'd embed in an appliance – were expensive and relatively rare. No longer! Today, manufacturers source powerful "System on a Chip" (SoC) processors at prices ranging from $0.25 to $8. These are full-fledged computers, easily capable of running an "access control" that satisfies DMCA 1201.
Likewise, in 1998, "access controls" (also called "DRM," "technical protection measures," etc) were a rarity in the field. That was because computer scientists broadly viewed these measures as useless. A determined adversary could always find a way around an access control, and they could package up that break as a software tool and costlessly, instantaneously distribute it over the internet to everyone in the world who wanted to do something that an access control impeded. Access controls were a stupid waste of engineering resources and a source of needless complexity and brittleness:
But – as critics pointed out in 1998 – chips were obviously going to get much cheaper, and if the US Congress made it a felony to bypass an access control, then every kind of manufacturer would be tempted to add some cheap SoCs to their products so they could add access controls and thereby felonize any uses of their products that cut into their profits. Basically, the DMCA offered manufacturers a bargain: add a dollar or two to the bill of materials for your product, and in return, the US government will imprison any competitors who offer your customers a "complementary good" that improves on it.
It's even worse than this: another thing that was obvious in 1998 was that once a manufacturer added a chip to a device, they would probably also figure out a way to connect it to the internet. Once that device is connected to the internet, the manufacturer can push software updates to it at will, which will be installed without user intervention. What's more, by using an access control in connection with that over-the-air update mechanism, the manufacturer can make it a felony to block its updates.
Which means that a manufacturer can sell you a device and then mandatorily update it at a later date to take away its functionality, and then sell that functionality back to you as a "subscription":
A thing that keeps happening:
And happening:
And happening:
In fact, it happens so often I've coined a term for it, "The Darth Vader MBA" (as in, "I'm altering the deal. Pray I don't alter it any further"):
Here's what this all means: any manufacturer who devotes a small amount of engineering work and incurs a small hardware expense can extinguish private property rights altogether.
What do I mean by private property? Well, we can look to Blackstone's 1753 treatise:
The right of property; or that sole and despotic dominion which one man claims and exercises over the external things of the world, in total exclusion of the right of any other individual in the universe.You can't own your iPhone. If you take your iPhone to Apple and they tell you that it is beyond repair, you have to throw it away. If the repair your phone needs involves "parts pairing" (where a new part won't be recognized until an Apple technician "initializes" it through a DMCA-protected access control), then it's a felony to get that phone fixed somewhere else. If Apple tells you your phone is no longer supported because they've updated their OS, then it's a felony to wipe the phone and put a different OS on it (because installing a new OS involves bypassing an "access control" in the phone's bootloader). If Apple tells you that you can't have a piece of software – like ICE Block, an app that warns you if there are nearby ICE killers who might shoot you in the head through your windshield, which Apple has barred from its App Store on the grounds that ICE is a "protected class" – then you can't install it, because installing software that isn't delivered via the App Store involves bypassing an "access control" that checks software to ensure that it's authorized (just like the toaster with its unauthorized bread).
It's not just iPhones: versions of this play out in your medical implants (hearing aid, insulin pump, etc); appliances (stoves, fridges, washing machines); cars and ebikes; set-top boxes and game consoles; ebooks and streaming videos; small appliances (toothbrushes, TVs, speakers), and more.
Increasingly, things that you actually own are the exception, not the rule.
And this is not normal. The end of ownership represents an overturn of a foundation of modern civilization. The fact that the only "people" who can truly own something are the transhuman, immortal colony organisms we call "Limited Liability Corporations" is an absolutely surreal reversal of the normal order of things.
It's a reversal with deep implications: for one thing, it means that you can't protect yourself from raids on your private data or ready cash by adding privacy blockers to your device, which would make it impossible for airlines or ecommerce sites to guess about how rich/desperate you are before quoting you a "personalized price":
It also means you can't stop your device from leaking information about your movements, or even your conversations – Microsoft has announced that it will gather all of your private communications and ship them to its servers for use by "agentic AI": (...)
Microsoft has also confirmed that it provides US authorities with warrantless, secret access to your data:
This is deeply abnormal. Sure, greedy corporate control freaks weren't invented in the 21st century, but the laws that let those sociopaths put you in prison for failing to arrange your affairs to their benefit – and your own detriment – are.
But because computers got faster and cheaper over decades, the end of ownership has had an incremental rollout, and we've barely noticed that it's happened. Sure, we get irritated when our garage-door opener suddenly requires us to look at seven ads every time we use the app that makes it open or close:
But societally, we haven't connected that incident to this wider phenomenon. It stinks here, but we're all used to it.
It's not normal to buy a book and then not be able to lend it, sell it, or give it away. Lending, selling and giving away books is older than copyright. It's older than publishing. It's older than printing. It's older than paper. It is fucking weird (and also terrible) (obviously) that there's a new kind of very popular book that you can go to prison for lending, selling or giving away.
We're just a few cycles away from a pair of shoes that can figure out which shoelaces you're using, or a dishwasher that can block you from using third-party dishes:
It's not normal, and it has profound implications for our security, our privacy, and our society. It makes us easy pickings for corporate vampires who drain our wallets through the gadgets and tools we rely on. It makes us easy pickings for fascists and authoritarians who ally themselves with corporate vampires by promising them tax breaks in exchange for collusion in the destruction of a free society.
I know that these problems are more important than whether or not we think this is normal. But still. It. Is. Just. Not. Normal.
by Cory Doctorow, Pluralistic | Read more:
Image: uncredited
Labels:
Business,
Copyright,
Crime,
Culture,
Design,
Economics,
Government,
Law,
Literature,
Media,
Politics,
Security,
Technology
Sunday, January 18, 2026
The Monkey’s Paw Curls
[ed. More than anyone probably wants to know (or can understand) about prediction markets.]
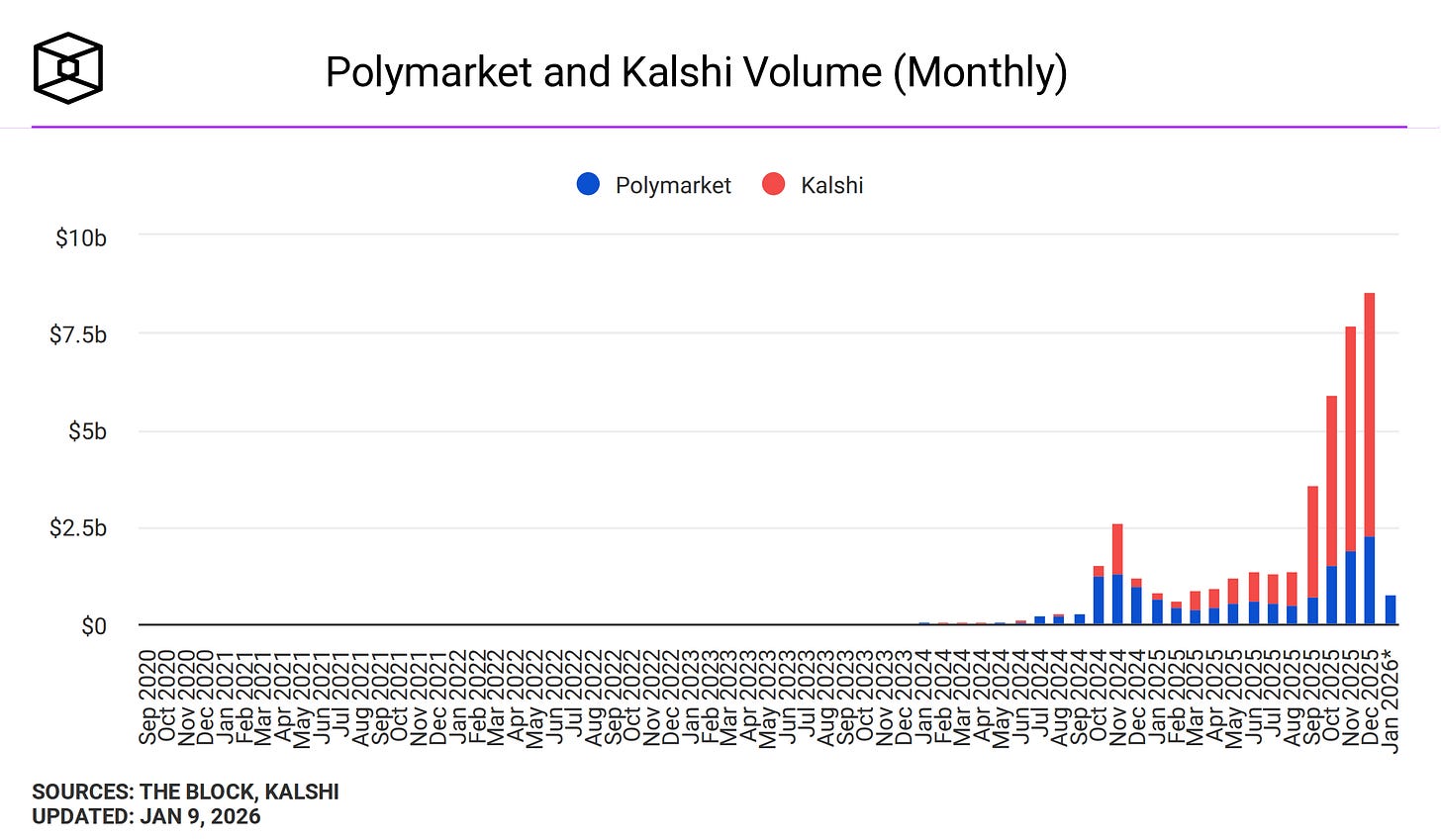
Since we last spoke, prediction markets have gone to the moon, rising from millions to billions in monthly volume.
For a few weeks in October, Polymarket founder Shayne Coplan was the world’s youngest self-made billionaire (now it’s some AI people). Kalshi is so accurate that it’s getting called a national security threat.
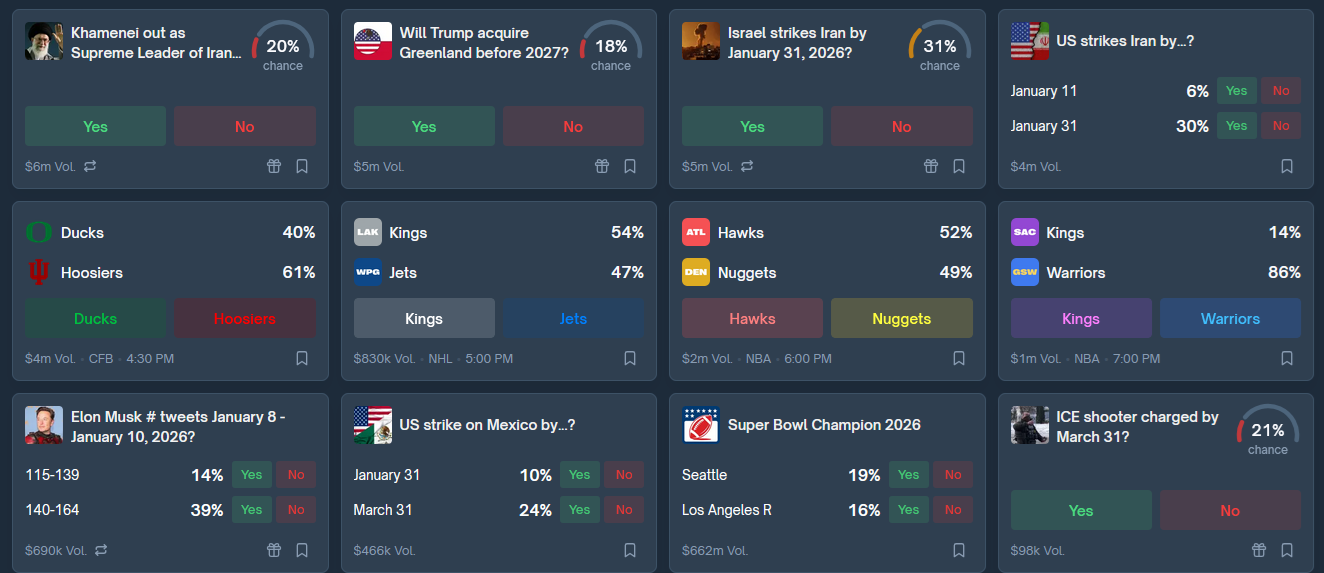
The catch is, of course, that it’s mostly degenerate gambling, especially sports betting. Kalshi is 81% sports by monthly volume. Polymarket does better - only 37% - but some of the remainder is things like this $686,000 market on how often Elon Musk will tweet this week - currently dominated by the “140 - 164 times” category.
(ironically, this seems to be a regulatory difference - US regulators don’t mind sports betting, but look unfavorably on potentially “insensitive” markets like bets about wars. Polymarket has historically been offshore, and so able to concentrate on geopolitics; Kalshi has been in the US, and so stuck mostly to sports. But Polymarket is in the process of moving onshore; I don’t know if this will affect their ability to offer geopolitical markets)
Degenerate gambling is bad. Insofar as prediction markets have acted as a Trojan Horse to enable it, this is bad. Insofar as my advocacy helped make this possible, I am bad. I can only plead that it didn’t really seem plausible, back in 2021, that a presidential administration would keep all normal restrictions on sports gambling but also let prediction markets do it as much as they wanted. If only there had been some kind of decentralized forecasting tool that could have given me a canonical probability on this outcome!
Still, it might seem that, whatever the degenerate gamblers are doing, we at least have some interesting data. There are now strong, minimally-regulated, high-volume prediction markets on important global events. In this column, I previously claimed this would revolutionize society. Has it?
I don’t feel revolutionized. Why not?
The problem isn’t that the prediction markets are bad. There’s been a lot of noise about insider trading and disputed resolutions. But insider trading should only increase accuracy - it’s bad for traders, but good for information-seekers - and my impression is that the disputed resolutions were handled as well as possible. When I say I don’t feel revolutionized, it’s not because I don’t believe it when it says there’s a 20% chance Khameini will be out before the end of the month. The several thousand people who have invested $6 million in that question have probably converged upon the most accurate probability possible with existing knowledge, just the way prediction markets should.
I actually like this. Everyone is talking about the protests in Iran, and it’s hard to gauge their importance, and knowing that there’s a 20% chance Khameini is removed by February really does help to place them in context. The missing link seems to be between “it’s now possible to place global events in probabilistic context → society revolutionized”.
Here are some possibilities:
Maybe people just haven’t caught on yet? Most news sources still don’t cite prediction markets, even when many people would care about their outcome. For example, the Khameini market hasn’t gotten mentioned in articles about the Iran protests, even though “will these protests succeed in toppling the regime?” is the obvious first question any reader would ask.
Maybe the problem is that probabilities don’t matter? Maybe there’s some State Department official who would change plans slightly over a 20% vs. 40% chance of Khameini departure, or an Iranian official for whom that would mean the difference between loyalty and defection, and these people are benefiting slightly, but not enough that society feels revolutionized.
Maybe society has been low-key revolutionized and we haven’t noticed? Very optimistically, maybe there aren’t as many “obviously the protests will work, only a defeatist doomer traitor would say they have any chance of failing!” “no, obviously the protests will fail, you’re a neoliberal shill if you think they could work” takes as there used to be. Maybe everyone has converged to a unified assessment of probabilistic knowledge, and we’re all better off as a result.
Maybe Polymarket and Kalshi don’t have the right questions. Ask yourself: what are the big future-prediction questions that important disagreements pivot around? When I try this exercise, I get things like:
- Will the AI bubble pop? Will scaling get us all the way to AGI? Will AI be misaligned?
- Will Trump turn America into a dictatorship? Make it great again? Somewhere in between?
- Will YIMBY policies lower rents? How much?
- Will selling US chips to China help them win the AI race?
- Will kidnapping Venezuela’s president weaken international law in some meaningful way that will cause trouble in the future?
- If America nation-builds Venezuela, for whatever definition of nation-build, will that work well, or backfire?
Annals of The Rulescucks
The new era of prediction markets has provided charming additions to the language, including “rulescuck” - someone who loses an otherwise-prescient bet based on technicalities of the resolution criteria.
Resolution criteria are the small print explaining what counts as the prediction market topic “happening'“. For example, in the Khameini example above, Khameini qualifies as being “out of power” if:
…he resigns, is detained, or otherwise loses his position or is prevented from fulfilling his duties as Supreme Leader of Iran within this market's timeframe. The primary resolution source for this market will be a consensus of credible reporting.You can imagine ways this definition departs from an exact common-sensical concept of “out of power” - for example, if Khameini gets stuck in an elevator for half an hour and misses a key meeting, does this count as him being “prevented from fulfilling his duties”? With thousands of markets getting resolved per month, chances are high that at least one will hinge upon one of these edge cases.
Kalshi resolves markets by having a staff member with good judgment decide whether or not the situation satisfies the resolution criteria.
Polymarket resolves markets by . . . oh man, how long do you have? There’s a cryptocurrency called UMA. UMA owners can stake it to vote on Polymarket resolutions in an associated contract called the UMA Oracle. Voters on the losing side get their cryptocurrency confiscated and given to the winners. This creates a Keynesian beauty contest, ie a situation where everyone tries to vote for the winning side. The most natural Schelling point is the side which is actually correct. If someone tries to attack the oracle by buying lots of UMA and voting for the wrong side, this incentivizes bystanders to come in and defend the oracle by voting for the right side, since (conditional on there being common knowledge that everyone will do this) that means they get free money at the attackers’ expense. But also, the UMA currency goes up in value if people trust the oracle and plan to use it more often, and it goes down if people think the oracle is useless and may soon get replaced by other systems. So regardless of their other incentives, everyone who owns the currency has an incentive to vote for the true answer so that people keep trusting the oracle. This system works most of the time, but tends towards so-called “oracle drama” where seemingly prosaic resolutions might lie at the end of a thrilling story of attacks, counterattacks, and escalations.
Here are some of the most interesting alleged rulescuckings of 2026:
Mr Ozi: Will Zelensky wear a suit? Ivan Cryptoslav calls this “the most infamous example in Polymarket history”. Ukraine’s president dresses mostly in military fatigues, vowing never to wear a suit until the war is over. As his sartorial notoriety spread, Polymarket traders bet over $100 million on the question of whether he would crack in any given month. At the Pope’s funeral, Zelensky showed up in a respectful-looking jacket which might or might not count. Most media organizations refused to describe it as a “suit”, so the decentralized oracle ruled against. But over the next few months, Zelensky continued to straddle the border of suithood, and the media eventually started using the word “suit” in their articles. This presented a quandary for the oracle, which was supposed to respect both the precedent of its past rulings, and the consensus of media organizations. Voters switched sides several times until finally settling on NO; true suit believers were unsatisfied with this decision. For what it’s worth, the Twitter menswear guy told Wired that “It meets the technical definition, [but] I would also recognize that most people would not think of that as a suit.”
[more examples...]
With one exception, these aren’t outright oracle failures. They’re honest cases of ambiguous rules.
Most of the links end with pleas for Polymarket to get better at clarifying rules. My perspective is that the few times I’ve talked to Polymarket people, I’ve begged them to implement various cool features, and they’ve always said “Nope, sorry, too busy figuring out ways to make rules clearer”. Prediction market people obsess over maximally finicky resolution criteria, but somehow it’s never enough - you just can’t specify every possible state of the world beforehand.
The most interesting proposal I’ve seen in this space is to make LLMs do it; you can train them on good rulesets, and they’re tolerant enough of tedium to print out pages and pages of every possible edge case without going crazy. It’ll be fun the first time one of them hallucinates, though.
With one exception, these aren’t outright oracle failures. They’re honest cases of ambiguous rules.
Most of the links end with pleas for Polymarket to get better at clarifying rules. My perspective is that the few times I’ve talked to Polymarket people, I’ve begged them to implement various cool features, and they’ve always said “Nope, sorry, too busy figuring out ways to make rules clearer”. Prediction market people obsess over maximally finicky resolution criteria, but somehow it’s never enough - you just can’t specify every possible state of the world beforehand.
The most interesting proposal I’ve seen in this space is to make LLMs do it; you can train them on good rulesets, and they’re tolerant enough of tedium to print out pages and pages of every possible edge case without going crazy. It’ll be fun the first time one of them hallucinates, though.
…And Miscellaneous N’er-Do-Wells
I include this section under protest.
The media likes engaging with prediction markets through dramatic stories about insider trading and market manipulation. This is as useful as engaging with Waymo through stories about cats being run over. It doesn’t matter whether you can find one lurid example of something going wrong. What matters is the base rates, the consequences, and the alternatives. Polymarket resolves about a thousand markets a month, and Kalshi closer to five thousand. It’s no surprise that a few go wrong; it’s even less surprise that there are false accusations of a few going wrong.
Still, I would be remiss to not mention this at all, so here are some of the more interesting stories:
by Scott Alexander, Astral Codex Ten | Read more:
Images: uncredited
Images: uncredited
Labels:
Business,
Design,
Economics,
Games,
Government,
Media,
Politics,
Technology
Friday, January 16, 2026
Measure Up
“My very dear friend Broadwood—
I have never felt a greater pleasure than in your honor’s notification of the arrival of this piano, with which you are honoring me as a present. I shall look upon it as an altar upon which I shall place the most beautiful offerings of my spirit to the divine Apollo. As soon as I receive your excellent instrument, I shall immediately send you the fruits of the first moments of inspiration I gather from it, as a souvenir for you from me, my very dear Broadwood; and I hope that they will be worthy of your instrument. My dear sir, accept my warmest consideration, from your friend and very humble servant.
—Ludwig van Beethoven”
As musical instruments improved through history, new kinds of music became possible. Sometimes, the improved instrument could make novel sounds; other times, it was louder; and other times stronger, allowing for more aggressive play. Like every technology, musical instruments are the fruit of generations worth of compounding technological refinement.
In a shockingly brief period between the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the piano was transformed technologically, and so too was the function of the music it produced.
To understand what happened, consider the form of classical music known as the “piano sonata.” This is a piece written for solo piano, and it is one of the forms that persisted through the transition, at least in name. In 1790, these were written for an early version of the piano that we now think of as the fortepiano. It sounded like a mix of a modern piano and a harpsichord.
Piano sonatas in the early 1790s were thought of primarily as casual entertainment. It wouldn’t be quite right to call them “background music” as we understand that term today—but they were often played in the background. People would talk over these little keyboard works, play cards, eat, drink.
In the middle of the 1790s, however, the piano started to improve at an accelerated rate. It was the early industrial revolution. Throughout the economy, many things were starting to click into place. Technologies that had kind of worked for a while began to really work. Scale began to be realized. Thicker networks of people, money, ideas, and goods were being built. Capital was becoming more productive, and with this serendipity was becoming more common. Few at the time could understand it, but it was the beginning of a wave—one made in the wake of what we today might call the techno-capital machine.
Riding this wave, the piano makers were among a great many manufacturers who learned to build better machines during this period. And with those improvements, more complex uses of those machines became possible.
Just as this industrial transformation was gaining momentum in the mid-1790s, a well-regarded keyboard player named Ludwig van Beethoven was starting his career in earnest. He, like everyone else, was riding the wave—though he, like everyone else, did not wholly understand it.
Beethoven was an emerging superstar, and he lived in Vienna, the musical capital of the world. It was a hub not just of musicians but also of musical instruments and the people who manufactured them. Some of the finest piano makers of the day—Walter, Graf, and Schanz—were in or around Vienna, and they were in fierce competition with one another. Playing at the city’s posh concert spaces, Beethoven had the opportunity to sample a huge range of emerging pianistic innovations. As his career blossomed, he acquired some of Europe’s finest pianos—including even stronger models from British manufacturers like Broadwood and Sons.
Iron reinforcement enabled piano frames with higher tolerances for louder and longer play. The strings became more robust. More responsive pedals meant a more direct relationship between the player and his tool. Innovations in casting, primitive machine tools, and mechanized woodworking yielded more precise parts. With these parts one could build superior hammer and escapement systems, which in turn led to faster-responding keys. And more of them, too—with higher and lower octaves now available. It is not just that the sound these pianos made was new: These instruments had an enhanced, more responsive user interface.
You could hit these instruments harder. You could play them softer, too. Beethoven’s iconic use of sforzando—rapid swings from soft to loud tones—would have been unplayable on the older pianos. So too would his complex and often rapid solos. In so many ways, then, Beethoven’s characteristic style and sound on the keyboard was technologically impossible for his predecessors to achieve...
Beethoven’s compositions for other instruments followed a structurally similar trajectory: compounding leaps in expressiveness, technical complexity, and thematic ambition, every few years. Here is what one of Mozart’s finest string quartets sounded like. Here is what Beethoven would do with the string quartet by the end of his career.
No longer did audiences talk during concerts. No longer did they play cards and make jokes. Audiences became silent and still, because what was happening to them in the concert hall had changed. A new type of art was emerging, and a new meta-character in human history—the artist—was being born. Beethoven was doing something different, something grander, something more intense, and the way listeners experienced it was different too.
The musical ideas Beethoven introduced to the world originated from his mind, but those ideas would have been unthinkable without a superior instrument.
I carried this laptop with me every day throughout the remainder of the pandemic. I ran a foundation using this laptop, and after that I orchestrated two career transitions using it. I built two small businesses, and I bought a house. I got married, and I planned a honeymoon with my wife. (...)
In a windowless office on a work trip to Stanford University on November 30, 2022, I discovered ChatGPT on this laptop. I stayed up all night in my hotel playing with the now-primitive GPT-3.5. Using my laptop, I educated myself more deeply about how this mysterious new tool worked.
I thought at first that it was an “answer machine,” a kind of turbocharged search engine. But I eventually came to prefer thinking of these language models as simulators of the internet that, by statistically modeling trillions of human-written words, learned new things about the structure of human-written text.
What might arise from a deeper-than-human understanding of the structures and meta-structures of nearly all the words humans have written for public consumption? What inductive priors might that understanding impart to this cognitive instrument? We know that a raw pretrained model, though deeply flawed, has quite sophisticated inductive priors with no additional human effort. With a great deal of additional human effort, we have made these systems quite useful little helpers, even if they still have their quirks and limitations.
But what if you could teach a system to guide itself through that digital landscape of modeled human thoughts to find better, rather than likelier, answers? What if the machine had good intellectual taste, because it could consider options, recognize mistakes, and decide on a course of cognitive action? Or what if it could, at least, simulate those cognitive processes? And what if that machine improved as quickly as we have seen AI advance so far? This is no longer science fiction; this research has been happening inside of the world’s leading AI firms, and with models like OpenAI’s o1 and o3, we see undoubtedly that progress is being made.
What would it mean for a machine to match the output of a human genius, word for word? What would it mean for a machine to exceed it? In at least some domains, even if only a very limited number at first, it seems likely that we will soon breach these thresholds. It is very hard to say how far this progress will go; as they say, experts disagree.
This strange simulator is “just math,”—it is, ultimately, ones and zeroes, electrons flowing through processed sand. But the math going on inside it is more like biochemistry than it is like arithmetic. The language model is, ultimately, still an instrument, but it is a strange one. Smart people, working in a field called mechanistic interpretability, are bettering our understanding all the time, but our understanding remains highly imperfect, and it will probably never be complete. We don’t quite have precise control yet over these instruments, but our control is getting better with time. We do not yet know how to make our control systems “good enough,” because we don’t quite know what “good enough” means yet—though here too, we are trying. We are searching.
As these instruments improve, the questions we ask them will have to get harder, smarter, and more detailed. This isn’t to say, necessarily, that we will need to become better “prompt engineers.” Instead, it is to suggest that we will need to become more curious. These new instruments will demand that we formulate better questions, and formulating better questions, often, is at least the seed of formulating better answers.
The input and the output, the prompt and the response, the question and the answer, the keyboard and the music, the photons and the photograph. We push at our instruments, we measure them up, and in their way, they measure us. (...)
I also think about the young Beethoven, playing around, trying to discover the capabilities of instruments with better keyboards, larger range, stronger frames, and suppler pedals. I think about all the uncoordinated work that had to happen—the collective and yet unplanned cultivation of craftsmanship, expertise, and industrial capacity—to make those pianos. I think about the staggering number of small industrial miracles that underpinned Beethoven’s keyboards, and the incomprehensibly larger number of industrial miracles that underpin the keyboard in front of me today. (...)
This past weekend, I replaced my MacBook Air with a new laptop. I wonder what it will be possible to do with this tremendous machine in a few years, or in a few weeks. New instruments for expression, and for intellectual exploration, will be built, and I will learn to use nearly all of them with my new laptop’s keyboard. It is now clear that a history-altering amount of cognitive potential will be at my fingertips, and yours, and everyone else’s. Like any technology, these new instruments will be much more useful to some than to others—but they will be useful in some way to almost everyone.
And just like the piano, what we today call “AI” will enable intellectual creations of far greater complexity, scale, and ambition—and greater repercussions, too. Higher dynamic range. I hope that among the instrument builders there will be inveterate craftsmen, and I hope that young Beethovens, practicing a wholly new kind of art, will emerge among the instrument players.
In 2026, this is no longer the case: there are now numerous substantive state AI bills floating around covering liability, algorithmic pricing, transparency, companion chatbots, child safety, occupational licensing, and more. In previous years, it was possible for me to independently cover most, if not all, of the interesting state AI bills at the level of rigor I expect of myself, and that my readers expect of me. This is no longer the case. There are simply too many of them.
I have never felt a greater pleasure than in your honor’s notification of the arrival of this piano, with which you are honoring me as a present. I shall look upon it as an altar upon which I shall place the most beautiful offerings of my spirit to the divine Apollo. As soon as I receive your excellent instrument, I shall immediately send you the fruits of the first moments of inspiration I gather from it, as a souvenir for you from me, my very dear Broadwood; and I hope that they will be worthy of your instrument. My dear sir, accept my warmest consideration, from your friend and very humble servant.
—Ludwig van Beethoven”
As musical instruments improved through history, new kinds of music became possible. Sometimes, the improved instrument could make novel sounds; other times, it was louder; and other times stronger, allowing for more aggressive play. Like every technology, musical instruments are the fruit of generations worth of compounding technological refinement.
In a shockingly brief period between the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the piano was transformed technologically, and so too was the function of the music it produced.
To understand what happened, consider the form of classical music known as the “piano sonata.” This is a piece written for solo piano, and it is one of the forms that persisted through the transition, at least in name. In 1790, these were written for an early version of the piano that we now think of as the fortepiano. It sounded like a mix of a modern piano and a harpsichord.
Piano sonatas in the early 1790s were thought of primarily as casual entertainment. It wouldn’t be quite right to call them “background music” as we understand that term today—but they were often played in the background. People would talk over these little keyboard works, play cards, eat, drink.
In the middle of the 1790s, however, the piano started to improve at an accelerated rate. It was the early industrial revolution. Throughout the economy, many things were starting to click into place. Technologies that had kind of worked for a while began to really work. Scale began to be realized. Thicker networks of people, money, ideas, and goods were being built. Capital was becoming more productive, and with this serendipity was becoming more common. Few at the time could understand it, but it was the beginning of a wave—one made in the wake of what we today might call the techno-capital machine.
Riding this wave, the piano makers were among a great many manufacturers who learned to build better machines during this period. And with those improvements, more complex uses of those machines became possible.
Just as this industrial transformation was gaining momentum in the mid-1790s, a well-regarded keyboard player named Ludwig van Beethoven was starting his career in earnest. He, like everyone else, was riding the wave—though he, like everyone else, did not wholly understand it.
Beethoven was an emerging superstar, and he lived in Vienna, the musical capital of the world. It was a hub not just of musicians but also of musical instruments and the people who manufactured them. Some of the finest piano makers of the day—Walter, Graf, and Schanz—were in or around Vienna, and they were in fierce competition with one another. Playing at the city’s posh concert spaces, Beethoven had the opportunity to sample a huge range of emerging pianistic innovations. As his career blossomed, he acquired some of Europe’s finest pianos—including even stronger models from British manufacturers like Broadwood and Sons.
Iron reinforcement enabled piano frames with higher tolerances for louder and longer play. The strings became more robust. More responsive pedals meant a more direct relationship between the player and his tool. Innovations in casting, primitive machine tools, and mechanized woodworking yielded more precise parts. With these parts one could build superior hammer and escapement systems, which in turn led to faster-responding keys. And more of them, too—with higher and lower octaves now available. It is not just that the sound these pianos made was new: These instruments had an enhanced, more responsive user interface.
You could hit these instruments harder. You could play them softer, too. Beethoven’s iconic use of sforzando—rapid swings from soft to loud tones—would have been unplayable on the older pianos. So too would his complex and often rapid solos. In so many ways, then, Beethoven’s characteristic style and sound on the keyboard was technologically impossible for his predecessors to achieve...
Beethoven was famous for breaking piano strings that were not yet strong enough to render his vision. There was always a relevant margin against which to press. By his final sonata, written in the early 1820s, he was pressing in the direction of early jazz. It was a technological and artistic takeoff from this to this, and from this to this.
Beethoven’s compositions for other instruments followed a structurally similar trajectory: compounding leaps in expressiveness, technical complexity, and thematic ambition, every few years. Here is what one of Mozart’s finest string quartets sounded like. Here is what Beethoven would do with the string quartet by the end of his career.
No longer did audiences talk during concerts. No longer did they play cards and make jokes. Audiences became silent and still, because what was happening to them in the concert hall had changed. A new type of art was emerging, and a new meta-character in human history—the artist—was being born. Beethoven was doing something different, something grander, something more intense, and the way listeners experienced it was different too.
The musical ideas Beethoven introduced to the world originated from his mind, but those ideas would have been unthinkable without a superior instrument.
—
I bought the instrument I’m using to write this essay in December 2020. I was standing in the frigid cold outside of the Apple Store in the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C., wearing a KN-95 face mask, separated by six feet from those next to me in line. I had dinner with a friend scheduled that evening. A couple weeks later, the Mayor would temporarily outlaw even that nicety.I carried this laptop with me every day throughout the remainder of the pandemic. I ran a foundation using this laptop, and after that I orchestrated two career transitions using it. I built two small businesses, and I bought a house. I got married, and I planned a honeymoon with my wife. (...)
In a windowless office on a work trip to Stanford University on November 30, 2022, I discovered ChatGPT on this laptop. I stayed up all night in my hotel playing with the now-primitive GPT-3.5. Using my laptop, I educated myself more deeply about how this mysterious new tool worked.
I thought at first that it was an “answer machine,” a kind of turbocharged search engine. But I eventually came to prefer thinking of these language models as simulators of the internet that, by statistically modeling trillions of human-written words, learned new things about the structure of human-written text.
What might arise from a deeper-than-human understanding of the structures and meta-structures of nearly all the words humans have written for public consumption? What inductive priors might that understanding impart to this cognitive instrument? We know that a raw pretrained model, though deeply flawed, has quite sophisticated inductive priors with no additional human effort. With a great deal of additional human effort, we have made these systems quite useful little helpers, even if they still have their quirks and limitations.
But what if you could teach a system to guide itself through that digital landscape of modeled human thoughts to find better, rather than likelier, answers? What if the machine had good intellectual taste, because it could consider options, recognize mistakes, and decide on a course of cognitive action? Or what if it could, at least, simulate those cognitive processes? And what if that machine improved as quickly as we have seen AI advance so far? This is no longer science fiction; this research has been happening inside of the world’s leading AI firms, and with models like OpenAI’s o1 and o3, we see undoubtedly that progress is being made.
What would it mean for a machine to match the output of a human genius, word for word? What would it mean for a machine to exceed it? In at least some domains, even if only a very limited number at first, it seems likely that we will soon breach these thresholds. It is very hard to say how far this progress will go; as they say, experts disagree.
This strange simulator is “just math,”—it is, ultimately, ones and zeroes, electrons flowing through processed sand. But the math going on inside it is more like biochemistry than it is like arithmetic. The language model is, ultimately, still an instrument, but it is a strange one. Smart people, working in a field called mechanistic interpretability, are bettering our understanding all the time, but our understanding remains highly imperfect, and it will probably never be complete. We don’t quite have precise control yet over these instruments, but our control is getting better with time. We do not yet know how to make our control systems “good enough,” because we don’t quite know what “good enough” means yet—though here too, we are trying. We are searching.
As these instruments improve, the questions we ask them will have to get harder, smarter, and more detailed. This isn’t to say, necessarily, that we will need to become better “prompt engineers.” Instead, it is to suggest that we will need to become more curious. These new instruments will demand that we formulate better questions, and formulating better questions, often, is at least the seed of formulating better answers.
The input and the output, the prompt and the response, the question and the answer, the keyboard and the music, the photons and the photograph. We push at our instruments, we measure them up, and in their way, they measure us. (...)
—
I don’t like to think about technology in the abstract. Instead, I prefer to think about instruments like this laptop. I think about all the ways in which this instrument is better than the ones that came before it—faster, more reliable, more precise—and why it has improved. And I think about the ways in which this same laptop has become wildly more capable as new software tools came to be. I wonder at the capabilities I can summon with this keyboard now compared with when I was standing in that socially distanced line at the Apple Store four years ago.I also think about the young Beethoven, playing around, trying to discover the capabilities of instruments with better keyboards, larger range, stronger frames, and suppler pedals. I think about all the uncoordinated work that had to happen—the collective and yet unplanned cultivation of craftsmanship, expertise, and industrial capacity—to make those pianos. I think about the staggering number of small industrial miracles that underpinned Beethoven’s keyboards, and the incomprehensibly larger number of industrial miracles that underpin the keyboard in front of me today. (...)
This past weekend, I replaced my MacBook Air with a new laptop. I wonder what it will be possible to do with this tremendous machine in a few years, or in a few weeks. New instruments for expression, and for intellectual exploration, will be built, and I will learn to use nearly all of them with my new laptop’s keyboard. It is now clear that a history-altering amount of cognitive potential will be at my fingertips, and yours, and everyone else’s. Like any technology, these new instruments will be much more useful to some than to others—but they will be useful in some way to almost everyone.
And just like the piano, what we today call “AI” will enable intellectual creations of far greater complexity, scale, and ambition—and greater repercussions, too. Higher dynamic range. I hope that among the instrument builders there will be inveterate craftsmen, and I hope that young Beethovens, practicing a wholly new kind of art, will emerge among the instrument players.
by Dean Ball, Hyperdimensional | Read more:
Image: 1827 Broadwood & Sons grand piano/Wikipedia[ed. Thoughtful essay throughout, well deserving of a full reading (even if you're just interested in Beethoven). On the hysterical end of the spectrum, here's what state legislators are proposing: The AI Patchwork Emerges. An update on state AI law in 2026 (so far) (Hyperdimensional):]
***
State legislative sessions are kicking into gear, and that means a flurry of AI laws are already under consideration across America. In prior years, the headline number of introduced state AI laws has been large: famously, 2025 saw over 1,000 state bills related to AI in some way. But as I pointed out, the vast majority of those laws were harmless: creating committees to study some aspect of AI and make policy recommendations, imposing liability on individuals who distribute AI-generated child pornography, and other largely non-problematic bills. The number of genuinely substantive bills—the kind that impose novel regulations on AI development or diffusion—was relatively small.In 2026, this is no longer the case: there are now numerous substantive state AI bills floating around covering liability, algorithmic pricing, transparency, companion chatbots, child safety, occupational licensing, and more. In previous years, it was possible for me to independently cover most, if not all, of the interesting state AI bills at the level of rigor I expect of myself, and that my readers expect of me. This is no longer the case. There are simply too many of them.
Labels:
Critical Thought,
Design,
history,
Music,
Philosophy,
Relationships,
Technology
Thursday, January 8, 2026
Wikipedia Style Guide
Many people edit Wikipedia because they enjoy writing; however, that passion can result in overlong composition. This reflects a lack of time or commitment to refine an effort through successively more concise drafts. With some application, natural redundancies and digressions can often be eliminated. Recall the venerable paraphrase of Pascal: "I made this so long because I did not have time to make it shorter." [Wikipedia: tl;dr]
Inverted pyramid
Image: Benjamin Busch/Import Projects - Wikimedia commons
Inverted pyramid
Some articles follow the inverted pyramid structure of journalism, which can be seen in news articles that get directly to the point. The main feature of the inverted pyramid is placement of important information first, with a decreasing importance as the article advances. Originally developed so that the editors could cut from the bottom to fit an item into the available layout space, this style encourages brevity and prioritizes information, because many people expect to find important material early, and less important information later, where interest decreases. (...)
What Wikipedia is not
Wikipedia is not a manual, guidebook, textbook, or scientific journal. Articles and other encyclopedic content should be written in a formal tone. Standards for formal tone vary depending upon the subject matter but should usually match the style used in Featured- and Good-class articles in the same category. Encyclopedic writing has a fairly academic approach, while remaining clear and understandable. Formal tone means that the article should not be written using argot, slang, colloquialisms, doublespeak, legalese, or jargon that is unintelligible to an average reader; it means that the English language should be used in a businesslike manner (e.g. use "feel" or "atmosphere" instead of "vibes").
News style or persuasive writing
A Wikipedia article should not sound like a news article. Especially avoid bombastic wording, attempts at humor or cleverness, over-reliance on primary sources, editorializing, recentism, pull quotes, journalese, and headlinese.
Similarly, avoid persuasive writing, which has many of those faults and more of its own, most often various kinds of appeals to emotion and related fallacies. This style is used in press releases, advertising, editorial writing, activism, propaganda, proposals, formal debate, reviews, and much tabloid and sometimes investigative journalism. It is not Wikipedia's role to try to convince the reader of anything, only to provide the salient facts as best they can be determined, and the reliable sources for them.
Wikipedia is not a manual, guidebook, textbook, or scientific journal. Articles and other encyclopedic content should be written in a formal tone. Standards for formal tone vary depending upon the subject matter but should usually match the style used in Featured- and Good-class articles in the same category. Encyclopedic writing has a fairly academic approach, while remaining clear and understandable. Formal tone means that the article should not be written using argot, slang, colloquialisms, doublespeak, legalese, or jargon that is unintelligible to an average reader; it means that the English language should be used in a businesslike manner (e.g. use "feel" or "atmosphere" instead of "vibes").
News style or persuasive writing
A Wikipedia article should not sound like a news article. Especially avoid bombastic wording, attempts at humor or cleverness, over-reliance on primary sources, editorializing, recentism, pull quotes, journalese, and headlinese.
Similarly, avoid persuasive writing, which has many of those faults and more of its own, most often various kinds of appeals to emotion and related fallacies. This style is used in press releases, advertising, editorial writing, activism, propaganda, proposals, formal debate, reviews, and much tabloid and sometimes investigative journalism. It is not Wikipedia's role to try to convince the reader of anything, only to provide the salient facts as best they can be determined, and the reliable sources for them.
Comparison of styles
via: Wikipedia: Writing better articlesImage: Benjamin Busch/Import Projects - Wikimedia commons
[ed. In celebration of Wikipedia Day (roughly Jan. 15). It's easy to forget how awesome this product really is: a massive, free, indispensable resource tended to by hundreds (thousands?) of volunteers simply for altruistic reasons. The best of the internet (and reminder of what could have been). See also: Wikipedia:What Wikipedia is not]
Labels:
Critical Thought,
Design,
Education,
Journalism,
Media,
Technology
Thursday, January 1, 2026
Leonardo’s Wood Charring Method Predates Japanese Practice
Yakisugi is a Japanese architectural technique for charring the surface of wood. It has become quite popular in bioarchitecture because the carbonized layer protects the wood from water, fire, insects, and fungi, thereby prolonging the lifespan of the wood. Yakisugi techniques were first codified in written form in the 17th and 18th centuries. But it seems Italian Renaissance polymath Leonardo da Vinci wrote about the protective benefits of charring wood surfaces more than 100 years earlier, according to a paper published in Zenodo, an open repository for EU funded research.
Check the notes
As previously reported, Leonardo produced more than 13,000 pages in his notebooks (later gathered into codices), less than a third of which have survived. The notebooks contain all manner of inventions that foreshadow future technologies: flying machines, bicycles, cranes, missiles, machine guns, an “unsinkable” double-hulled ship, dredges for clearing harbors and canals, and floating footwear akin to snowshoes to enable a person to walk on water. Leonardo foresaw the possibility of constructing a telescope in his Codex Atlanticus (1490)—he wrote of “making glasses to see the moon enlarged” a century before the instrument’s invention.
In 2003, Alessandro Vezzosi, director of Italy’s Museo Ideale, came across some recipes for mysterious mixtures while flipping through Leonardo’s notes. Vezzosi experimented with the recipes, resulting in a mixture that would harden into a material eerily akin to Bakelite, a synthetic plastic widely used in the early 1900s. So Leonardo may well have invented the first manmade plastic.
The notebooks also contain Leonardo’s detailed notes on his extensive anatomical studies. Most notably, his drawings and descriptions of the human heart captured how heart valves can control blood flow 150 years before William Harvey worked out the basics of the human circulatory system. (In 2005, a British heart surgeon named Francis Wells pioneered a new procedure to repair damaged hearts based on Leonardo’s heart valve sketches and subsequently wrote the book The Heart of Leonardo.)
In 2023, Caltech researchers made another discovery: lurking in the margins of Leonardo’s Codex Arundel were several small sketches of triangles, their geometry seemingly determined by grains of sand poured out from a jar. The little triangles were his attempt to draw a link between gravity and acceleration—well before Isaac Newton came up with his laws of motion. By modern calculations, Leonardo’s model produced a value for the gravitational constant (G) to around 97 percent accuracy. And Leonardo did all this without a means of accurate timekeeping and without the benefit of calculus. The Caltech team was even able to re-create a modern version of the experiment.
“Burnt Japanese cedar”
Annalisa Di Maria, a Leonardo expert with the UNESCO Club of Florence, collaborated with molecular biologist and sculptor Andrea da Montefeltro and art historian Lucica Bianchi on this latest study, which concerns the Codex Madrid II. They had noticed one nearly imperceptible phrase in particular on folio 87r concerning wood preservation: “They will be better preserved if stripped of bark and burned on the surface than in any other way,” Leonardo wrote.
“This is not folklore,” the authors noted. “It is a technical intuition that precedes cultural codification.” Leonardo was interested in the structural properties of materials like wood, stone, and metal, as both an artist and an engineer, and would have noticed from firsthand experience that raw wood with its bark intact retained moisture and decayed more quickly. Furthermore, Leonardo’s observation coincides with what the authors describe as a “crucial moment for European material culture,” when “woodworking was receiving renewed attention in artistic workshops and civil engineering studies.”
Leonardo did not confine his woody observations to just that one line. The Codex includes discussions of how different species of wood conferred different useful properties: oak and chestnut for strength, ash and linden for flexibility, and alder and willow for underwater construction. Leonardo also noted that chestnut and beech were ideal as structural reinforcements, while maple and linden worked well for constructing musical instruments given their good acoustic properties. He even noted a natural method for seasoning logs: leaving them “above the roots” for better sap drainage.
The Codex Madrid II dates to 1503-1505, over a century before the earliest known written codifications of yakisugi, although it is probable that the method was used a bit before then. Per Di Maria et al., there is no evidence of any direct contact between Renaissance European culture and Japanese architectural practices, so this seems to be a case of “convergent invention.”
The benefits of this method of wood preservation have since been well documented by science, although the effectiveness is dependent on a variety of factors, including wood species and environmental conditions. The fire’s heat seals the pores of the wood so it absorbs less water—a natural means of waterproofing. The charred surface serves as natural insulation for fire resistance. And stripping the bark removes nutrients that attract insects and fungi, a natural form of biological protection.
by Jennifer Ouellette, Ars Technica | Read more:
Images: A. Di maria et al., 2025; Unimoi/CC BY-SA 4.0; and Lorna Satchell/CC BY 4.0
Check the notes
As previously reported, Leonardo produced more than 13,000 pages in his notebooks (later gathered into codices), less than a third of which have survived. The notebooks contain all manner of inventions that foreshadow future technologies: flying machines, bicycles, cranes, missiles, machine guns, an “unsinkable” double-hulled ship, dredges for clearing harbors and canals, and floating footwear akin to snowshoes to enable a person to walk on water. Leonardo foresaw the possibility of constructing a telescope in his Codex Atlanticus (1490)—he wrote of “making glasses to see the moon enlarged” a century before the instrument’s invention.
In 2003, Alessandro Vezzosi, director of Italy’s Museo Ideale, came across some recipes for mysterious mixtures while flipping through Leonardo’s notes. Vezzosi experimented with the recipes, resulting in a mixture that would harden into a material eerily akin to Bakelite, a synthetic plastic widely used in the early 1900s. So Leonardo may well have invented the first manmade plastic.
The notebooks also contain Leonardo’s detailed notes on his extensive anatomical studies. Most notably, his drawings and descriptions of the human heart captured how heart valves can control blood flow 150 years before William Harvey worked out the basics of the human circulatory system. (In 2005, a British heart surgeon named Francis Wells pioneered a new procedure to repair damaged hearts based on Leonardo’s heart valve sketches and subsequently wrote the book The Heart of Leonardo.)
In 2023, Caltech researchers made another discovery: lurking in the margins of Leonardo’s Codex Arundel were several small sketches of triangles, their geometry seemingly determined by grains of sand poured out from a jar. The little triangles were his attempt to draw a link between gravity and acceleration—well before Isaac Newton came up with his laws of motion. By modern calculations, Leonardo’s model produced a value for the gravitational constant (G) to around 97 percent accuracy. And Leonardo did all this without a means of accurate timekeeping and without the benefit of calculus. The Caltech team was even able to re-create a modern version of the experiment.
“Burnt Japanese cedar”
Annalisa Di Maria, a Leonardo expert with the UNESCO Club of Florence, collaborated with molecular biologist and sculptor Andrea da Montefeltro and art historian Lucica Bianchi on this latest study, which concerns the Codex Madrid II. They had noticed one nearly imperceptible phrase in particular on folio 87r concerning wood preservation: “They will be better preserved if stripped of bark and burned on the surface than in any other way,” Leonardo wrote.
“This is not folklore,” the authors noted. “It is a technical intuition that precedes cultural codification.” Leonardo was interested in the structural properties of materials like wood, stone, and metal, as both an artist and an engineer, and would have noticed from firsthand experience that raw wood with its bark intact retained moisture and decayed more quickly. Furthermore, Leonardo’s observation coincides with what the authors describe as a “crucial moment for European material culture,” when “woodworking was receiving renewed attention in artistic workshops and civil engineering studies.”
Leonardo did not confine his woody observations to just that one line. The Codex includes discussions of how different species of wood conferred different useful properties: oak and chestnut for strength, ash and linden for flexibility, and alder and willow for underwater construction. Leonardo also noted that chestnut and beech were ideal as structural reinforcements, while maple and linden worked well for constructing musical instruments given their good acoustic properties. He even noted a natural method for seasoning logs: leaving them “above the roots” for better sap drainage.
The Codex Madrid II dates to 1503-1505, over a century before the earliest known written codifications of yakisugi, although it is probable that the method was used a bit before then. Per Di Maria et al., there is no evidence of any direct contact between Renaissance European culture and Japanese architectural practices, so this seems to be a case of “convergent invention.”
The benefits of this method of wood preservation have since been well documented by science, although the effectiveness is dependent on a variety of factors, including wood species and environmental conditions. The fire’s heat seals the pores of the wood so it absorbs less water—a natural means of waterproofing. The charred surface serves as natural insulation for fire resistance. And stripping the bark removes nutrients that attract insects and fungi, a natural form of biological protection.
Images: A. Di maria et al., 2025; Unimoi/CC BY-SA 4.0; and Lorna Satchell/CC BY 4.0
Labels:
Architecture,
Culture,
Design,
Environment,
history,
Science
Wednesday, December 31, 2025
Wednesday, December 17, 2025
Feast Your Eyes on Japan’s Fake Food
Japanese people like to say that they “eat with their eyes,” relishing the colors, shapes, and textures of a dish before it ever hits the tongue. The phrase applies all the more when the dish in question isn’t meant to be eaten at all. Last year, I was one of two hundred thousand people to visit “Looks Delicious!,” an exhibition organized by the cultural center Japan House London showcasing dozens upon dozens of shokuhin sampuru—mesmerizingly lifelike handmade food replicas that appear in the windows and display cases of restaurants, kiosks, and bars across Japan. Shokuhin sampuru are a roughly ninety-million-dollar industry, and a beloved part of Japanese pop culture. A few decades ago, there was a show on Japanese television in which shokuhin sampuru artisans competed to make the most convincing replicas of dishes, a sort of inverse of “Is It Cake?”
But, according to Japan House, “Looks Delicious!” marks the first time that a cultural institution has dedicated a show exclusively to food replicas. The exhibition originated last year at London’s Japan House and became its most popular show ever—perhaps in part because shokuhin sampuru feel especially pertinent in a political-cultural environment that so often confounds the real and the fake. In September, the show travelled to the Los Angeles branch of Japan House, on Hollywood Boulevard, where it will run until the end of January. A sidewalk full of stars has got nothing, in my opinion, on a stencil used to apply dark-meat detail to the muscle near a mackerel’s spine.
Early shokuhin sampuru were relatively rough replicas molded out of wax; some pioneering artisans were more accustomed to, say, sculpting ear canals for otologists and solar systems for science classes. Even in rudimentary form, they freed customers from having to badger employees with questions or take their chances ordering a bowl of ramen, not knowing whether it would come with two slices of pork or three. Food replicas eased embarrassment, prevented disappointment, and encouraged experimentation, just as they do today. “The Japanese customer loves to know what they’re getting,” the food writer Yukari Sakamoto told me. “When I’m meeting up with my family in Tokyo, we talk and talk and look at the plastic food displays until something jumps out at us.”
The first business dedicated to the manufacture and sale of shokuhin sampuru was founded in 1932 in Osaka by Iwasaki Takizō, one of the craft’s original three practitioners. A native of Gujō Hachiman, a town in the central prefecture of Gifu, he became enthralled by wax during his boyhood. Legend has it that he got the idea for food replicas after watching a candle melt into cold water, its drippings hardening into the shape of blooming flowers. Today, the Iwasaki Group is responsible for about seventy per cent of food replicas sold in Japan...
“Looks Delicious!” focusses on the period beginning in the nineteen-twenties, when Western food began to make inroads in Japan, and restaurateurs—particularly in Tokyo department stores—used replicas to communicate efficiently to prospective clients what, exactly, “spaghetti” or “ham sandwich” entailed. Later, shokuhin sampuru also came to be associated with kissaten—cozy, smoke-filled cafés featuring European décor and menu items like buttered toast and strawberry shortcake. “These food replicas have this very retro, Shōwa period, nineteen-fifties-and-sixties vibe,” Wright said. If they remained somewhat crude in this era—they couldn’t be tilted, for example, lest the wax soften and start to droop in the sun—their popularity didn’t suffer. By 1958, the Iwasaki Group was exporting a passable rib eye to the United States, to be used as a promotional item by a beer company.
Japan House is funded by the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, so it’s perhaps unsurprising that the exhibition’s organizers hit upon a clever way to emphasize the diversity of food replicas and promote tourism at the same time. An entire section is dedicated to regional cuisines—a dish for each of the country’s forty-seven prefectures. There is kiritanpo nabe from the mountains of Akita, a hot-pot dish featuring mashed rice wrapped around a cedar stick and baked, and a fish-and-fiddlehead-fern ohaw, a soup from the Ainu people, who live mainly in Hokkaido. I haven’t been able to stop thinking about the mouthwatering simulacrum of sudachi-sōmen—wheat-flour noodles in chicken broth, topped with a light-green citrus fruit that grows in Tokushima. (...)
However persuasive they might be as facsimiles, shokuhin sampuru are subjective interpretations, seeking not only to replicate dishes but to intensify the feelings associated with the real thing. Nose told me, “It’s like augmented reality created by skilled artisans. I think this is the magic of replica food.” A replica of red-bean paste, for example, might be grainier than actual red-bean paste, because people tend to associate red-bean paste with graininess. A kiwi might be fuller and greener than usual, because the person who made it likes her fruit especially ripe. Liquids are among the most difficult foodstuffs to render, and leafy greens, raw meats, and emulsions are where real artistry is unleashed. One of the ultimate tests of virtuosity for a shokuhin sampuru maker is said to be whipped cream.
[ed. For many more examples, see also: Photos show hyper-realistic plastic food that is a $90 million industry in Japan (MYSA).]
But, according to Japan House, “Looks Delicious!” marks the first time that a cultural institution has dedicated a show exclusively to food replicas. The exhibition originated last year at London’s Japan House and became its most popular show ever—perhaps in part because shokuhin sampuru feel especially pertinent in a political-cultural environment that so often confounds the real and the fake. In September, the show travelled to the Los Angeles branch of Japan House, on Hollywood Boulevard, where it will run until the end of January. A sidewalk full of stars has got nothing, in my opinion, on a stencil used to apply dark-meat detail to the muscle near a mackerel’s spine.
Shokuhin sampuru can be wondrously intricate: iridescent slivers of shrimp; striated sirloins with fatty crusts; bouncy poached eggs on the brink of first ooze; cross-sections of cabbage with the labyrinthine swirls of an elevation map; a banana split with two scoops of chocolate ice cream, their granularity evoking just a whisper of freezer burn. So it is a bit surprising that “Looks Delicious!” begins with, of all things, a humble sack of yellow onions. Simon Wright, the director of programming at Japan House London, told me, during a tour of the gallery, that a different kind of exhibit might have begun with “a whole gantry of sushi,” but that he preferred the alliums for their exuberant plainness. “Remember those strings of plastic onions that might have hung in a restaurant in the nineteen-eighties?” he said. “These are nothing like them.” (...)
According to Yasunobu Nose, a Japanese journalist who has written extensively about shokuhin sampuru, food replicas first appeared in Japan in the nineteen-twenties and thirties, when three men started simultaneously producing them in three different cities. This coincidence, Nose explains, was a result of urbanization, which brought workers to big cities, where they began to buy more of their meals outside the home. As early as the Edo period, Japanese people “decided what to eat by looking at real food,” Nose said in a recent lecture at Japan House London. While researching shokuhin sampuru, he found a nineteenth-century genre painting depicting a street festival where merchants displayed actual dishes of sushi and tempura outside their stalls. Shokuhin sampuru were a pragmatic innovation, allowing venders to follow the same long-standing custom without wasting their actual food.
According to Yasunobu Nose, a Japanese journalist who has written extensively about shokuhin sampuru, food replicas first appeared in Japan in the nineteen-twenties and thirties, when three men started simultaneously producing them in three different cities. This coincidence, Nose explains, was a result of urbanization, which brought workers to big cities, where they began to buy more of their meals outside the home. As early as the Edo period, Japanese people “decided what to eat by looking at real food,” Nose said in a recent lecture at Japan House London. While researching shokuhin sampuru, he found a nineteenth-century genre painting depicting a street festival where merchants displayed actual dishes of sushi and tempura outside their stalls. Shokuhin sampuru were a pragmatic innovation, allowing venders to follow the same long-standing custom without wasting their actual food.
Early shokuhin sampuru were relatively rough replicas molded out of wax; some pioneering artisans were more accustomed to, say, sculpting ear canals for otologists and solar systems for science classes. Even in rudimentary form, they freed customers from having to badger employees with questions or take their chances ordering a bowl of ramen, not knowing whether it would come with two slices of pork or three. Food replicas eased embarrassment, prevented disappointment, and encouraged experimentation, just as they do today. “The Japanese customer loves to know what they’re getting,” the food writer Yukari Sakamoto told me. “When I’m meeting up with my family in Tokyo, we talk and talk and look at the plastic food displays until something jumps out at us.”
The first business dedicated to the manufacture and sale of shokuhin sampuru was founded in 1932 in Osaka by Iwasaki Takizō, one of the craft’s original three practitioners. A native of Gujō Hachiman, a town in the central prefecture of Gifu, he became enthralled by wax during his boyhood. Legend has it that he got the idea for food replicas after watching a candle melt into cold water, its drippings hardening into the shape of blooming flowers. Today, the Iwasaki Group is responsible for about seventy per cent of food replicas sold in Japan...
“Looks Delicious!” focusses on the period beginning in the nineteen-twenties, when Western food began to make inroads in Japan, and restaurateurs—particularly in Tokyo department stores—used replicas to communicate efficiently to prospective clients what, exactly, “spaghetti” or “ham sandwich” entailed. Later, shokuhin sampuru also came to be associated with kissaten—cozy, smoke-filled cafés featuring European décor and menu items like buttered toast and strawberry shortcake. “These food replicas have this very retro, Shōwa period, nineteen-fifties-and-sixties vibe,” Wright said. If they remained somewhat crude in this era—they couldn’t be tilted, for example, lest the wax soften and start to droop in the sun—their popularity didn’t suffer. By 1958, the Iwasaki Group was exporting a passable rib eye to the United States, to be used as a promotional item by a beer company.
Japan House is funded by the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, so it’s perhaps unsurprising that the exhibition’s organizers hit upon a clever way to emphasize the diversity of food replicas and promote tourism at the same time. An entire section is dedicated to regional cuisines—a dish for each of the country’s forty-seven prefectures. There is kiritanpo nabe from the mountains of Akita, a hot-pot dish featuring mashed rice wrapped around a cedar stick and baked, and a fish-and-fiddlehead-fern ohaw, a soup from the Ainu people, who live mainly in Hokkaido. I haven’t been able to stop thinking about the mouthwatering simulacrum of sudachi-sōmen—wheat-flour noodles in chicken broth, topped with a light-green citrus fruit that grows in Tokushima. (...)
However persuasive they might be as facsimiles, shokuhin sampuru are subjective interpretations, seeking not only to replicate dishes but to intensify the feelings associated with the real thing. Nose told me, “It’s like augmented reality created by skilled artisans. I think this is the magic of replica food.” A replica of red-bean paste, for example, might be grainier than actual red-bean paste, because people tend to associate red-bean paste with graininess. A kiwi might be fuller and greener than usual, because the person who made it likes her fruit especially ripe. Liquids are among the most difficult foodstuffs to render, and leafy greens, raw meats, and emulsions are where real artistry is unleashed. One of the ultimate tests of virtuosity for a shokuhin sampuru maker is said to be whipped cream.
by Lauren Collins, New Yorker | Read more:
Images: via; and Masuda Yoshirо̄/Courtesy Japan House
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)